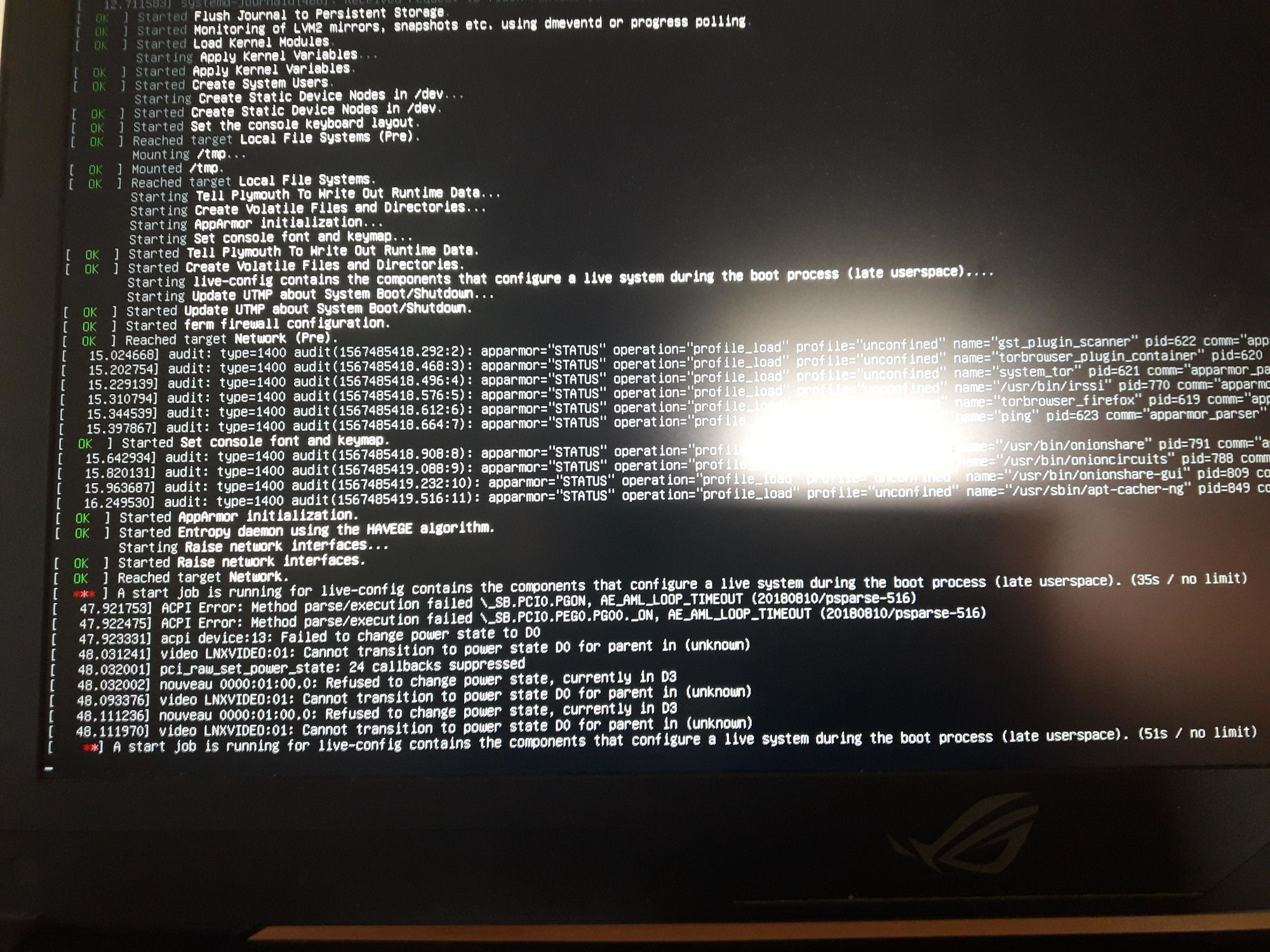
A start job is running for wait for network to be configured
A start job is running for wait for network to be configured
Ubuntu Server 18.04 ожидает сеть при запуске, хотя сеть в порядке
У меня свежая установка Ubuntu Server 18.04. Пока все не настроено и не протестировано, я хочу, чтобы он был подключен как к проводной, так и к Wi-Fi сети.
Мой каталог /etc/netplan содержит два файла:
Когда сервер загружается, он остается в течение 2 минут с этим сообщением:
Пока отображается это сообщение, сервер может проверять связь по проводному IP, но не по Wi-Fi. Его можно пропинговать по Wi-Fi IP сразу после того, как пройдут 2 минуты ожидания, и на подключенном дисплее отобразится приглашение пользователя.
Когда я вхожу в систему, ifconfig показывает, что оба интерфейса нормально инициализированы: оба получили свои IP-адреса от маршрутизатора, сервер доступен по сети на обоих IP-адресах.
Вот вывод networkctl list Команда сразу после загрузки:
Wi-Fi маршрутизатор находится на расстоянии около 2 метров, сигнал очень сильный. Поскольку я не планирую слишком много перезагружать сервер, проблема ожидания терпима. Но я боюсь, что это может быть признаком некоторой конфигурации сети, которую следует исправить, прежде чем все станет плохо.
1 ответ
Что делать, если вы добавите
к вашей конфигурации wifis/wlp58s0? У меня была похожая проблема, но только когда я загружался без проводного Ethernet. Содержание моего /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml (мой единственный файл в этом каталоге) был
A start job is running for wait for network to be configured. Ubuntu server 17.10
i just installed ubuntu server on my laptop and everything works fine except for the fact that at boot if the laptop is not connected to ethernet or in range of my wi-fi i get this message «A start job is running for wait for network to be configured» that stays for about 2 minutes. I looked up online for solutions and i tried to:
None of these solutions worked for me. Any possible fixes?
7 Answers 7
Don’t mask or disable the systemd service.
Edit /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml and add optional: true to any devices that may not always be available.
to disable the wait-online service to prevent the system from waiting on a network connection, and use
to prevent the service from starting if requested by another service (the service is symlinked to /dev/null ).
This means systemd-networkd-wait-online.service is hanging. There’s a few known bugs with it. Check what services want network-online.target with:
You can disable those services if you want. Otherwise, you may have to mask the service as Mr.Ecco indicated.
I run into this problem because I use a dynamic fail-over setup for my devices with bonding the wired (e.g. enp9s0) and wireless (e.g. wlp12s0) interface that are used as slaves for the main interface bond0. Exactly the same situation do you have if you use a bridge (br0 with slave interfaces). Only the main interfaces bond0 or br0 will get online but not the slaves so systemd-networkd-wait-online.service will fail on the slaves.
The solution to this problem is to modify the service and ignore the interfaces that are slaves and does not signal to be online. You will find with:
In the empty editor insert these statements, of course with your interface names, save them an quit the editor:
The empty ExecStart= is important because it disables the «old» command. You can check for more than one interface (look at the help).
Ubuntu 18.04/Server boot delay > 2MIN every time («A start job is running for Wait for Network to be Configured») #773
Comments
holta commented May 2, 2018 •
IIAB 6.5/master (big local_vars.yml) was installed on a clean Ubuntu 18.04/Server on NUC.
Every boot is delayed by more than 2MIN with this msg:
Thanks @jvonau and @georgejhunt if you can investigate (currently at 10.8.0.30).
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
holta commented May 2, 2018
FYI this 2MIN delay does not occur on similar (but not identical!) NUC 10.8.0.22
Likely unrelated:
PR #772 «Remove br0 in Appliance Mode for NetworkManager (e.g. if no internal WiFi)»
holta commented May 3, 2018
@jvonau used the above to confirmed a manual workaround.
FYI the 2MIN hang (or lack thereof) can be traced after the fact using:
-b = current boot
-l = ellipsize fields when they do not fit in available columns
—no-pager = disable page-by-page output, for grep etc
-u = how messages for the specified systemd unit UNIT (such as a service unit), or for any of the units matched by PATTERN
holta commented May 3, 2018
It’s been reconfirmed that the installation of IIAB 6.5/master does indeed bring about this 2MIN-hang-on-boot problem.
Задание запуска работает за ожиданием сети, которая будет настроена. Сервер Ubuntu 17.10
я просто установил сервер человечности на своем ноутбуке, и все хорошо работает за исключением того, что при начальной загрузке, если ноутбук не подключен к Ethernet или в диапазоне моего Wi-Fi, я добираюсь, это сообщение «Задание запуска работает за ожиданием сети, которая будет настроена», который остается в течение приблизительно 2 минут. Я искал решения онлайн, и я пытался:
Ни одно из этих решений не работало на меня. Кто-либо возможные меры?
7 ответов
, чтобы отключить службу ожидания в режиме онлайн, чтобы система не ожидала подключения к сети, и используйте
, чтобы предотвратить запуск службы по запросу другим сервисом (сервис связан с /dev/null ).
Это означает systemd-networkd-wait-online.service зависает. Существует несколько известных ошибок с ним. Проверьте то, что хотят сервисы network-online.target с:
Можно отключить те сервисы, если Вы хотите. Иначе Вам, вероятно, придется замаскировать сервис, как г-н Ecco указал.
Не маскируйте или отключайте systemd сервис.
Править /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml и добавьте optional: true к любым устройствам, которые не могут всегда быть доступными.
Я сталкиваюсь с этой проблемой, потому что я использую динамическую установку обработки отказа для своих ноутбуков со связыванием проводного (enp9s0) и беспроводная связь (wlp12s0) интерфейс, которые используются в качестве ведомых устройств для основного интерфейса bond0. Точно та же ситуация делает Вы имеете при использовании моста (br0 с ведомыми интерфейсами). Только основные интерфейсы bond0 или br0 станут онлайн, но не ведомые устройства так systemd-networkd-wait-online.service перестанет работать на ведомых устройствах.
Решение этой проблемы состоит в том, чтобы изменить сервис и проверить только на интерфейсы, которые должны пойти онлайн. Вы найдете с:
В пустом редакторе вставляют эти операторы, конечно, с Вашим интерфейсом, сохраняют их выход редактор:
Пустое ExecStart= важно, потому что это отключает «старую» команду. Можно проверить на больше, чем в интерфейсе (посмотрите на справку).
Ubuntu 18.04.1 does not boot without ethernet cable
This is my /etc/network/interfaces :
This is my /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml :
When the machine is connected to the network, it boots up fine. But whenever I take it over to my desk for maintenance, where there is no network cable, I am greeted with this:
A start job is running for Wait for Network to be Configured
How can I fix this, so I can boot the machine without an ethernet cable attached?
1 Answer 1
I usually see this when I use static ip addresses on my virtual machines. As the networkd needs to setup your network or add your system to the network using this values so if the network isn’t available it won’t boot.
Modify your configurations and add the optional: true to prevent the system from wating during boot.
Prevent waiting for interface Interfaces that are not required for booting or should not be waited on during boot should have the optional: true key added to them. This will prevent long delays in booting for interfaces that may not come up.
Почему Netplan/Networkd не поднимает статический интерфейс Ethernet?
У меня есть машина рабочий Сервер Ubuntu 18.04. Сеть настроена с помощью Netplan, таким образом, у меня есть эта конфигурация в /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml :
enp1s0f0 подключен к устройству, которое может или не может работать (при начальной загрузке или никакое другое время). Я хочу выполнить сервер DHCP в этом интерфейсе.
Проблема, когда я загружаюсь существует задержка нескольких минут, и я вижу это сообщение:
В конечном счете это испытывает таймаут, начальная загрузка продолжается, но enp1s0f0 никогда не настраивается или поднимается. ip link show enp1s0f0 дает:
Теперь, если я включаю подключенное устройство, конечно же enp1s0f0 подходит:
Но это бесполезно в этой точке — сервер DHCP не будет работать, потому что это не могло запуститься с enp1s0f0 нет во время начальной загрузки. Мне нужно enp1s0f0 и настроенный во время начальной загрузки, которая я думал, был смысл статической конфигурации IP. Еще более странный то, что это всегда имеет адрес IPv6, даже когда это снижается:
Если я проверяю вывод отладки Netplan, я вижу:
Моя конфигурация для isc-dhcp-server должен иметь /etc/default/isc-dhcp-server содержите:
. и /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf содержите (среди других вещей):
Это не было проблемой под ifupdown (Я понятия не имею почему enp1s0f0 только подходит во время начальной загрузки, является ли что-нибудь в другом конце кабеля; я думал, что это было смыслом наличия статического IP). Действительно ли возможно получить его работающий в Netplan? Или действительно ли возможно иметь сервер DHCP, запускаются когда enp1s0f0 произошел?
Arch Linux
You are not logged in.
#1 2014-12-25 02:26:07
[SOLVED]»A start job is running for Wait for Network to be Configured»
Every time I boot my laptop and there is no known WiFi networks nearby, it hangs on this message: «A start job is running for Wait for Network to be Configured». When there is a known network nearby, it boots just fine. So whenever I travel somewhere and attempt to boot my system, it hangs forever (which really sucks 
I suspect I must have enabled some systemd task that requires a network connection, causing the computer not to boot until a connection is present. Has anyone ever seen that message before? Or, does anyone have some pointers to jobs I could check?
I’ve been stuck on this issue for about a week so any help would be much appreciated.
Last edited by ryanjacobs (2014-12-27 04:06:35)
Задание запуска выполняется для ожидания настройки сети. Ubuntu сервер 17.10
Я только что установил сервер Ubuntu на моем ноутбуке, и все работает нормально, за исключением того факта, что при загрузке, если ноутбук не подключен к Ethernet или в зоне действия моего Wi-Fi, я получаю это сообщение «Запускается задание для ожидания подключения к сети быть настроенным «, который остается около 2 минут. Я искал онлайн решения и попытался:
Ни одно из этих решений не помогло мне. Любые возможные исправления?
отключить службу ожидания в режиме онлайн, чтобы система не ожидала подключения к сети, и использовать
запретить запуск службы по запросу другой службы (служба имеет символическую ссылку /dev/null ).
Не маскируйте и не отключайте службу systemd.
Отредактируйте /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml и добавьте optional: true на любые устройства, которые не всегда могут быть доступны.
Это значит systemd-networkd-wait-online.service висит. Есть несколько известных ошибок с этим. Проверьте, какие услуги нужны network-online.target с:
Решением этой проблемы является изменение службы и проверка только на наличие интерфейсов, которые должны быть подключены к сети. Вы найдете с:
В пустом редакторе вставьте эти операторы, конечно же, с вашим интерфейсом, сохраните их и выйдите из редактора:
Пустое ExecStart= значение важно, потому что оно отключает «старую» команду. Вы можете проверить больше, чем на интерфейсе (посмотрите на помощь).
Ubuntu Server 18.04 waiting for Network at startup although the network is ok
I have fresh installation of Ubuntu Server 18.04. Until it is all set up and tested, I want it to be connected to both wired and wifi network.
My /etc/netplan directory contains two files:
When the server boots up, it stays for 2 minutes on this message:
While this message is displayed, the server can be pinged over the wired IP, but not over the wifi IP. It can be pinged over the wifi IP right after the 2 minutes of waiting have passed and user prompt is displayed on the connected display.
When I log on, ifconfig shows that both interfaces have initialized fine: both have received their IP addresses from the router, the server is reachable over the network at both IPs.
Here’s the output of networkctl list command right after boot:
The wifi router is about 2 meters close, the signal is very strong. Since I don’t plan to restart the server too much, the problem of waiting is bearable. But I am afraid this could be a symptom of some network configuration that should be fixed before things get bad.
Very long startup time on Ubuntu Server (network configuration)
I’ve been trying to sort out two problems that I suspect are interrelated. Recently, our network got reconfigured and afterward, I encountered a very long boot time due to network configuration issues and, after booting, no longer able to access the samba file share from a Win10 client.
The boot time messages:
It takes about two minutes for the last message to clear. I suspect it’s maybe a DHCP or DNS-related issue. I’ve also noticed several of the «NXDOMAIN / potential DVE2018-0001 violation» errors interspersed in /var/log/syslog. At the moment, I really don’t know where to go poking next to figure out what’s causing this delay (or why the file server isn’t visible to Win10 clients). Incidentally, Samba appears to be running and Webmin reports that the folder share is active.
EDIT 1:
Per the suggestion of @heynnema in the comments, the output of cat /etc/netplan/*.yaml :
Сервер Ubuntu 18,04 ожидания Сети при запуске, хотя сеть в порядке
У меня есть новая установка Сервера Ubuntu 18.04. Пока это все не настраивается и тестируется, я хочу, чтобы это было подключено к соединенной проводом сети и с сети Wi-Fi.
Мой/etc/netplan каталог содержит два файла:
50 облаков init.yaml:
Когда сервер загружается, это остается в течение 2 минут на этом сообщении:
В то время как это сообщение отображено, сервер может быть проверен с помощью ping-запросов по проводному IP, но не по IP Wi-Fi. Это может быть проверено с помощью ping-запросов по IP Wi-Fi прямо после того, как 2 минуты ожидания передали, и пользовательская подсказка отображена на подключенном дисплее.
Когда я вхожу в систему, ifconfig показывает, что оба интерфейса инициализировали прекрасный: оба получили их IP-адреса от маршрутизатора, сервер достижим по сети на уровне обоих дюйм/с.
Вот вывод networkctl list команда прямо после начальной загрузки:
Маршрутизатор Wi-Fi составляет приблизительно 2 метра близко, сигнал очень силен. Так как я не планирую перезапустить сервер слишком много, проблема ожидания терпима. Но я боюсь, что это могло быть признаком некоторой конфигурации сети, которая должна быть зафиксирована, прежде чем вещи становятся плохими.
Why is Netplan/Networkd not bringing up a static ethernet interface?
I have a machine running Ubuntu Server 18.04. The network is configured using Netplan, so I have this config in /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml :
enp1s0f0 is connected to a device that may or may not be on (at boot or any other time). I want to run a DHCP server on this interface.
The trouble is, when I boot there’s a delay of a few minutes and I see this message:
Eventually it times out, the boot continues, but enp1s0f0 is never configured or brought up. ip link show enp1s0f0 gives:
Now if I turn the attached device on, sure enough enp1s0f0 comes up:
But it’s of no use at this point — the DHCP server won’t work, because it couldn’t start with enp1s0f0 no up at boot time. I need enp1s0f0 up and configured during boot, which I thought was the whole point of a static IP configuration. Even stranger is that it always has an IPv6 address, even when it’s down:
If I check Netplan’s debug output, I see:
My configuration for isc-dhcp-server is to have /etc/default/isc-dhcp-server contain:
. and /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf contain (amongst other things):
This wasn’t an issue under ifupdown (I have no idea why enp1s0f0 doesn’t just come up during boot, whether or not anything is at the other end of the cable; I thought that was the whole point of having a static IP). Is it possible to get it working in Netplan? Or is it possible to have the DHCP server start when enp1s0f0 is up?
WiFi interface configured as AP is down after system restart
I’m trying to setup my WiFi interface in AP mode using hostapd. However, after system restart startup hangs for about 2min on:
It seems that WiFi interface is not getting UP and that is why systemd-networkd-wait-online.service hangs. It does not if I set WiFi interface as ignored in systemd-networkd-wait-online.service, but this does not solve the general problem.
After system startup I see this output after I execute ip addr command:
As I expected interface is DOWN.
sudo ip link set wlxc04a0010118a up does not change interface status. To bring it UP and fix my issue I have to execute systemctl restart hostapd.service
Then ip addr command returns:
I would like to fix that and have WiFi AP configured after system startup without this manual step as other services rely on this interface and eventualy have to be also started manualy when interface is up. I tried many things but still cannot solve this. I would appreciate your help.
What does NetworkManager-wait-online.service do?
NetworkManager-wait-online.service fails at boot and it delays my startup
4 Answers 4
Some code runs off the network
In some multi-user environments part of the boot-up process can come from the network. For this case systemd defaults to waiting for the network to come on-line before certain steps are taken.
Majority of Desktop Users
Unlike some multi-user environments most Ubuntu desktop users have the Operating System and drivers on their hard disks, SSDs or Live Boot USBs.
There is a glitch where some users wait an extremely long time for network to come up during boot. In this case the recommendations is to set the maximum wait time to 30 seconds. A better way is to simply disable the service at boot time.
For many users 10 to 15 seconds can be sliced off the parallel boot time by using:
After you sign on you will likely get a message bubble stating you’ve now been connected to the network (WiFi or Ethernet access to Internet).
It appears that this service simply waits, doing absolutely nothing, until the network is connected, and when this happens, it changes its state so that other services that depend on the network can be launched to start doing their thing.
So, it appears that this service is absolutely benign, it does not waste any time during boot, and it actually constitutes an optimization, so you are only going to make things worse if you disable it.
(Services that need the network will start before the network is up, at a time when many other services are also starting up and contention is high, and these services will be unable to do anything useful, so they will just keep retrying to connect to the network, until the network finally comes up.)
«A start job is running for Raise network interfaces» Windows 10 host, Ubuntu 16.04 guest #8056
Comments
samwho commented Nov 29, 2016
Please note that the Vagrant issue tracker is reserved for bug reports and
enhancements. For general usage questions, please use the Vagrant mailing list:
https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/vagrant-up. Thank you!
Vagrant version
Virtualbox version
Host operating system
Guest operating system
Vagrantfile
Please note, if you are using Homestead or a different Vagrantfile format, we
may be unable to assist with your issue. Try to reproduce the issue using a
vanilla Vagrantfile first.
Debug output
Expected behavior
The virtual machine should boot without any problem and I should land in an SSH session with it.
Actual behavior
The «vagrant up» command times out waiting for the machine to boot. The machine does eventually boot, but it spends the full 5 minutes and 4 seconds waiting for «A start job is running for Raise network interfaces».
Interestingly, if I boot the machine from virtualbox rather than running «vagrant up», it boots fine and all of the networking stuff works. This is what leads me to believe that this is a vagrant bug.
Steps to reproduce
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
tembra commented Dec 16, 2016 •
This error occurs because the Ubuntu tries to raise all your network interfaces, but your cable isn’t connected, then he waits until his timeout.
It seems that this problem occurs when you export a VM, more info on https://www.virtualbox.org/ticket/15705
You have two ways to solve this issue:
I recommend first solution 🙂
For other people to known, I have this issue on laravel/homestead box. Tried to update everything, but only this solution above worked.
line on vendor/laravel/homestead/scripts/homestead.rb file at # Configure A Few VirtualBox Settings section loop.
My system configuration:
samwho commented Dec 16, 2016
tembra commented Dec 16, 2016
Your Vagrantfile should look like this:
On Windows these files are default stored at C:\Users\xxx\VirtualBox VMs where xxx is you username.
If the first one didn’t work, now try to find the definition files and try second solution.
samwho commented Dec 16, 2016
tembra commented Dec 18, 2016 •
Hmm.. too much strange!
If this didn’t work try to update VirtualBox to latest version (same as mine).
I only tested these commands after updated VBox, because I was thinking that should be a VBox problem.
It seems that this problem occurs when you export a VM, more info on https://www.virtualbox.org/ticket/15705
I also added this info on first post.
samwho commented Dec 18, 2016
Here’s what I get after making your suggested change:
I’ll try updating to the latest VirtualBox.
samwho commented Dec 18, 2016
I updated to 5.1.10 r112026 and at first tried removing the modifyvm stuff in my Vagrantfile to see if it would work without it. It did not, I got the same problem about waiting to raise network interfaces at startup.
I added the following back in:
config.vm.provider «virtualbox» do |vb|
vb.customize [«modifyvm», :id, «—cableconnected1», «on»]
end
And there’s no difference, still waits 5 solid minutes at startup.
I changed cableconnected1 to cableconnected0 and got the same error as in my previous reply to this issue.
In short, updating changed none of the behaviour I had previously seen.
tembra commented Dec 18, 2016 •
Sorry guy but I don’t know how to help you. I did not experience any issue after make these changes.
alquesadilla commented Dec 30, 2016
tembra your solution worked for me with option 1. Thank you and God Bless
jdomenechb commented Jan 5, 2017 •
Same problem for me. I have Windows 7 host and Ubuntu 16.04 as guest.
I am suspecting a firewall setting, as the machine boots up normally when using the host Ethernet adapter, but the issue described there is reproduced if I try to use the host WiFi connection instead. However, as it is a corporative computer, I cannot test nor change the configuration of the firewall in any way.
anthonyblazejack commented Jan 18, 2017
The first solution @tembra posted worked for me as well. Thank you!
lamnguyenx commented Jan 22, 2017
I can confirm that the 1st solution of @tembra worked for me. Ty 👍
TrimA74 commented Feb 20, 2017 •
@tembra solution work only when i’m using Wifi and ethernet connection.
When i’m offline, i got the issue with the job Raise Network Interfaces during 5min 6 sec.
I have Windows 8.1 and i’m using Homestead
hoanganh25991 commented Jun 27, 2017 •
@tembra solution 1 works for me
Add vb.customize in provider
On windows 7, my computer has wifi connection.
I haven’t test if both ethernet & wifi is off.
kikitux commented Jul 20, 2017
So multiples versions of vagrant and virtualbox have happened
The cabbkle connect was an issue in some VirtualBox versions.
esafzay commented Aug 23, 2017
VirtualBox 5.1.26 r117224 (Qt5.6.2)
Ubuntu 17.04 as VM
When network type is ‘Internal Network’ I am getting this message in the boot:
A start job is running for Raise network interfaces
@tembra ‘s second solution did not work for me.
lesliemayer commented Nov 1, 2017
I was able resolve this issue by enabling virtualization in the BIOS of my PC.
blairharper commented Apr 12, 2018
This thread is a bit old but it’s the top link on google when searching for the error term + vagrant. I just want to add that enabling CPU virtualisation in the BIOS also fixed this error for me. I had dismissed this solution initially and spent hours trying out the some of the others and searching multiple sites.
Check your BIOS settings, make sure virtualisation is enabled!
navndn commented Apr 12, 2018
I can vagrant up and vagrant ssh into guest VM hashicorp/precise64 but I get timeout error with ubuntu/xenial64 as guest.
Adding this didn’t solved the problem for me
Does the BIOS setting that you’re suggesting applies to GCP-VMs too?
Another thread where I commented earlier- #9608
blairharper commented Apr 12, 2018
@navndn I’m no expert on GCP VMs (or VMs at all really) but I would be surprised if they didn’t have the necessary virtualisation system settings in place.
Having read the GCP guidance you linked (the «Restrictions» and «Tested KVM versions» sections) I suspect that ubuntu/xenial64 is just not supported/working properly for nested virtualisation.
temp1029 commented Jul 28, 2018 •
For others looking here and myself when I inevitably forget how to fix this in the future (since it is the top hit on Google), I was able to get around this by following the instructions here:
Specifically I used the ‘mask’ option. It seems like a poor solution to me, given it disables a feature versus fixing the error, but after many hours of work and no luck, I was happy just to get it up. Also, there seem to be some issues with that particular service in Ubuntu anyways, so maybe it is best just to turn it off.
Using this I did not need the ‘cableconnected1’ config lines either.
My setup details if helpful:
Host: Windows 8
Provider: VirtualBox 5.2.16
Guest OS: Ubuntu 17.10
Vagrant: 2.1.2
ghost commented Apr 1, 2020
If you have found a problem that seems similar to this, please open a new issue and complete the issue template so we can capture all the details necessary to investigate further.
After upgrading to 20.04 LTS, network now takes 2 minutes to start because of cloud-init
Further digging shows:
/etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/ contains some files that are 4+ years old:
Are the files in /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d supposed to be removed or updated at some point?
This textbox defaults to using Markdown to format your answer.
You can type !ref in this text area to quickly search our full set of tutorials, documentation & marketplace offerings and insert the link!
These answers are provided by our Community. If you find them useful, show some love by clicking the heart. If you run into issues leave a comment, or add your own answer to help others.
Want to learn more? Join the DigitalOcean Community!
Join our DigitalOcean community of over a million developers for free! Get help and share knowledge in Q&A, subscribe to topics of interest, and get courses and tools that will help you grow as a developer and scale your project or business.
Long bootup time with bridge configured in netplan in 18.04
In Ubuntu 18.04 the default network configuration is done with netplan. I have a setup which creates a bridge interface at startup, see below.
It all works great, except that during startup it runs into a timeout of about 2 minutes. After the timeout it finishes the startup, and the system runs without problems.
For 2 minutes it prints this message on the console (also present in /var/log/boot.log)
I have several systems with Ubuntu 18.04 and netplan, but only the ones with a this bridge interface have this problem.
Does anyone else see this too?
This is my netplan config
BTW. I’m using this bridge for LXD. At startup there are no LXD containers yet that use this bridge.
1 Answer 1
Just stumbled upon this exact problem. In my case it was because one of the interfaces in the bridge didn’t have a network cable plugged in so networkd/networkctl tried to get it up (because it is defined in netplan) but failed.
I would guess that not having it defined at all in your netplan configuration causes the same issue. Perhaps networkd/networkctl is waiting for a «link is up» signal from a bridge that will never send one because there is no interface in it?
The solution in my case was to add optional: true in the interface definition (not the bridge).
In your case, with a bridge without any interface, the solution might be to do it at the bridge level:
For good measure I added the directive to all interfaces in that bridge.
Thread: A start job is running for raise network interfaces (5 mins 1 sec) in ubuntu16.04
Thread Tools
Display
A start job is running for raise network interfaces (5 mins 1 sec) in ubuntu16.04
i have installed ubuntu 16.04 in my laptop.
starting ubuntu is fast when i have LAN cabled connected.
when LAN cable disconnected then it is taking around 5 minutes to get login screen.
it was showing this message with timer on screen at that long time.
«A start job is running for raise network interfaces (2 minutes of 5 mins 1 sec)»
1) how can i skip this delay (5 mins for waiting network).
like if there are some shortcut keys which i typed then the startup script should not wait for 5 mins, it should directly skip the network interface checking and go to login screen.
or
2) how can i permanently stop network interface check only when LAN cable not connected.
Re: A start job is running for raise network interfaces (5 mins 1 sec) in ubuntu16.04
The system is set up to make a wired connection to the router and to do that automatically. But is cannot complete the task because the ethernet cable is disconnected. So, it tries again and again until finally some part of the OS gets the message.
There should be an icon on the top panel for the Network Manager. With the cable connected the icon will be two arrows going in the opposite direction. With the cable disconnected the icon will look like an upside down cone. Click on the icon; select Edit Connections; Select Wired Connection; Click Edit; Go to the General tab and untick the box labelled «Automatically connect to this network when it is available.»
In future when you want to make a wired connection to the router, then Click on the Network Manager icon and untick & re-tick Enable Networking. That should prompt Network Manager to start making the wired connection to the router.
It is a machine. It is more stupid than we are. It will not stop us from doing stupid things.
Ubuntu user #33,200. Linux user #530,530
I have a Debian 10 Server that I think could/should boot faster, but I don’t know what the problem is.
I see A start job is running for Raise network interfaces when booting, and looking at systemd-analyze blame it seems a lot of time is spend in networking.service (I left out the services below 50ms).
Doing a systemctl stop networking.service and systemctl start networking.service takes less than 2 seconds though.
This is my /etc/network/interfaces for reference (br0 is used for VMs):
32 seconds with allow-hotplug (probably because the interfaces are started in parallel?), and I get a console immediately without the A start job is running message. Changing br0 to it made that interface not start automatically though, so I left it.
Also only when auto is active on the enp* interfaces, I get A stop job is running for Raise network interfaces on shutdown, which takes about 50 seconds to complete.
So I want to know if it’s OK to leave the interfaces on allow-hotplug (maybe there can be interface binding issues for some services?), and if there are any other problems I can fix to improve boot times.
Debian User Forums
[SOLVED] start job running for LSB: Raise network interface
[SOLVED] start job running for LSB: Raise network interface
#1 Post by hughparker1 » 2016-02-11 20:45
I have just installed debian-live-8.3.0-i386-lxde on my old hp530 32-bit laptop
with the 3 asterisks above moving back and forth.
. then it boots OK into operating system. so apart from the delay everything is working ok.
Has anyone seen this kind of message before, and is there a way to avoid this delay? I am still learning linux but if someone can point me in the right direction I would be grateful. I can use terminal if I know the syntax to use. Thanks for any assistance.
Re: [***]A start job is running for LSB: Raise network inter
#2 Post by spacex » 2016-02-11 23:26
As root, open «etc/network/interfaces».
If there is a line with «allow hotplug», then comment it out, save and reboot. If this doesn’t apply to your issue, then report back.
Re: [***]A start job is running for LSB: Raise network inter
#3 Post by hughparker1 » 2016-02-11 23:46
Re: [***]A start job is running for LSB: Raise network inter
#4 Post by Head_on_a_Stick » 2016-02-12 07:42
Does your ISP offer IPv6?
If not, remove that line.
«It seems that UNIX has become the victim of cancerous growth at the hands of organizations such as UCB. 4.2BSD is an order of magnitude larger than Version 5, but, Pike claims, not ten times better.»
— Murray Hill, Bell Laboratories
Re: [***]A start job is running for LSB: Raise network inter
#5 Post by hughparker1 » 2016-02-12 09:54
From the output, it looks like my ISP does not offer IPv6? I don’t have the technical knowledge to analyse the test output properly. My ISP is TalkTalk in UK.
Re: [***]A start job is running for LSB: Raise network inter
#6 Post by Head_on_a_Stick » 2016-02-12 18:07
«It seems that UNIX has become the victim of cancerous growth at the hands of organizations such as UCB. 4.2BSD is an order of magnitude larger than Version 5, but, Pike claims, not ten times better.»
— Murray Hill, Bell Laboratories
Re: [***]A start job is running for LSB: Raise network inter
#7 Post by hughparker1 » 2016-02-12 20:43
Any idea what might be wrong?
Another thing that puzzles me is sometimes when I start the laptop, I find I am not connected to the wireless router, even though I have saved the wireless key and made sure the option
Automatically connect to this network = enabled
It doesn’t happen every time but it has happened four times today.
I find I need to open Wicd Network Manager and click ‘Switch on Wi-Fi’ then click ‘Refresh’ button along the top of the Manager window. Then I see the wireless networks and then need to click Connect button each time.
Why is ssh too slow when I access in Ubuntu 18.04?
I’ve recently installed Ubuntu 18.04 and set the network and I configured NIS client to get user information from the server.
The problem is when I access this server through ssh, it is too slow to get a shell from the server. I’ve been digging out to solve this problem and found this error message from /var/log/auth.log but I don’t know how to do that. What should I do?
1 Answer 1
This problem is induced by the network interface, netplan, which is newly adapted in Ubuntu 18.04. Usually, when users configure this interface, they put optional: true attribute in the *.yaml to set an ethernet like below.
The reason why they put that attr is because if there is no attr in the file, it will hang in a certain amount of time on boot showing the message.
But the problem is that when you put this attr, an optional instruction in /etc/pam.d/common-session runs and this makes an error while you are trying to make a connection to the server
So, you need to comment out to get rid of time out while making a connection or session with the server.
Speeding 21.04 server boot by specifying network config
I recently installed server 21.04 on some new hardware. I’m using it at home, mostly for some dev experiments.
I don’t understand everything that happens when the system is booted, but it takes much longer than I expect. When I start the boot sequence, I notice one message that takes far longer to clear than any other:
This is followed on the next line by:
I guess this means that the server is waiting for network addresses to be assigned? That should be handled by the modem / wifi box provided by my ISP? It seems to handle all the other wired and wireless connections without any trouble.
This is in the output from ifconfig:
I can’t read this in any detail, but it seems okay? There’s an IP4 and an IP6 address granted, and I can connect to the server over SSH by IP4 address or by name.
This is the output from systemd-analyze:
I guess this is far too long in userspace for most systems?
Can you suggest possible causes for this long wait? How can I investigate further?
EDIT: This is the output from cat /etc/netplan/*.yaml (there is only one file in that directory):
The directory /etc/network/interfaces is empty.
Stable IT
FastNetMon
Sunday, 26 December 2021
The start job is running for Wait For Network to be configured with Ubuntu 20.04
I’ve got this issue on Digital Ocean VM with Ubuntu 20.04. Apparently, it started happening after minor upgrade via apt-get update / apt-get upgrade.
Full text of error:
And network did not start at all. In console I was able to see that eth0 is active but had no IP. I think this issue is related with some cloud-init bugs triggered by upgrade.
I was able to fix it short term via KVM / recovery console by trying sudo ifdown eth0 and then sudo ifup eth0 but it failed again after reboot.
As long term fix I’ve disabled cloud-init via special file:
Then it fixed network configuration but did not address 2 minute delay before ssh start.
Debian User Forums
«A start job is running for Raise network interfaces» SOLVED
«A start job is running for Raise network interfaces» SOLVED
#1 Post by jaimet » 2019-07-19 09:50
I’ve just installed a fresh Buster (debian 10) on a dell studio 1555 (using the netinst non-free CD image) and the install went perfectly. I’ve edited /etc/network/interfaces to add a stanza for my «Qualcomm Atheros AR928X Wireless Network Adapter (PCI-Express)» nic (pci id: 168c:002a), thus:
I then reboot. During the boot, I see «A start job is running for Raise network interfaces» and a counter which counts up for between approx 90 and 120 seconds, after which the boot completes.
How can I debug this delay/pause? (I don’t understand how raising the network interface can take so long if the ifup completes so quickly).
Edited 1st October: it turns out that my «boot delay» / «slow boot» / «boot pause» problem was just another instance of the «Boottime Entropy Starvation» issue. (I’m guessing that wpa-supplicant couldn’t connect as it was blocking on requesting random data from the kernel, which in turn was blocking on the entropy generator).
Re: «A start job is running for Raise network interfaces»
#2 Post by ruwolf » 2019-07-19 17:30
Re: «A start job is running for Raise network interfaces»
#3 Post by Deb-fan » 2019-07-20 06:21
Probably better just to use some type of networking software to do it for you. Long way from a gnu/nix wifi networking guru but my personal preference has long been using ceni, handy bunch of scripts, ncurses interface that supports easy scanning for available Hotspots and am told now available in stock Buster repos, I’ve long been snagging it from Siduction gnu/Linux repos for Debian stable or other branches. Ie: Sid.
Off the top guess, having a conflict among services/packages trying to manage your network interfaces they may need to be masked w systemctl, ie: systemd-networkd or if Network-manager (Gnome) thing installed and running. Remember long ago setting it up similar to what you’re doing, directly editing /etc/network/interfaces and having somewhat similar issues. Don’t recall the specifics, wasnt a start job, was a stop job and nowhere near as drastic as what you’re experiencing but was hanging for 20-30secs at shutdown. Installed and using ceni, happy with using it.
Re: «A start job is running for Raise network interfaces»
#4 Post by jaimet » 2019-07-20 07:19
I tried it anyway, with the following result:
auto: the boot hangs (pauses) while the counter counts up, thereby delaying the completion of the boot process/the appearance of the login screen.
allow-hotplug: the boot completes quickly (the login screen appears quickly) but if I log-in and immediately test the networking connection, it hasn’t yet connected. At some point in the next minute, the networking connection is made.
This makes me think that «allow-hotplug» makes raising the network interface happen in parallel/asynchronously, whereas «auto» makes raising the network interface happen synchronously (i.e. as a blocking process).
Thank you for the suggestion anyway!
Re: «A start job is running for Raise network interfaces»
#5 Post by jaimet » 2019-07-20 07:31
Thank you for the pointer re ceni, but I personally prefer to keep the number of packages installed to a complete minimum, so I’ll just accept the boot delay. At some point, I’ll find the time to learn how to debug the boot procedure. Thanks again.
Re: «A start job is running for Raise network interfaces»
#6 Post by Head_on_a_Stick » 2019-07-20 10:20
You do have systemd-networkd installed, it is part of the systemd package so you could try that and see if it brings your network up any quicker.
To debug ifupdown try
Once it is all set up then enable the service with
«It seems that UNIX has become the victim of cancerous growth at the hands of organizations such as UCB. 4.2BSD is an order of magnitude larger than Version 5, but, Pike claims, not ten times better.»
— Murray Hill, Bell Laboratories
Re: «A start job is running for Raise network interfaces»
#7 Post by jaimet » 2019-08-03 15:55
Re: «A start job is running for Raise network interfaces»
#8 Post by Head_on_a_Stick » 2019-08-03 17:14
«It seems that UNIX has become the victim of cancerous growth at the hands of organizations such as UCB. 4.2BSD is an order of magnitude larger than Version 5, but, Pike claims, not ten times better.»
— Murray Hill, Bell Laboratories
Re: «A start job is running for Raise network interfaces»
#9 Post by jaimet » 2019-08-19 11:16
and then rebooted, but I still get the same delay.
I’ve noticed that during the boot process, the following error message appears:
Re: «A start job is running for Raise network interfaces»
#10 Post by arzgi » 2019-08-19 15:51
I changed it to 20 secs.
To disable ipv6, as root
My computers are behind nat, no use to ipv6, that’s why I allways disable it. I’m not sure if it speeds up raising network.
Re: «A start job is running for Raise network interfaces»
#11 Post by Head_on_a_Stick » 2019-08-19 16:29
The ip command should always show the IPv6 link-local address, perhaps that’s what you’re seeing there.
You can disable the IPv6 stack with the ipv6.disable=1 kernel command line parameter.
«It seems that UNIX has become the victim of cancerous growth at the hands of organizations such as UCB. 4.2BSD is an order of magnitude larger than Version 5, but, Pike claims, not ten times better.»
Working internet access / network bridge on Ubuntu running virtual machine?
Please consider the following scenario.
Host: Ubuntu 18.04 LTS desktop with latest updates. QEMU version 3.1.
Network managed by network-manager with working wireless connection to the Internet.
Please note that neither libvirt nor tools like uvtool or multipass should be used.
Issue: I can’t get any working network connection to the host. Neither qemu-bridge-helper nor Ubuntu server guide or any of the proposals I read here in StackExchange provided a working solution.
Error message upon launch of the VM:
qemu-system-x86_64: could not configure /dev/net/tun: Operation not permitted
Launching the VM as root provides:
W: /etc/qemu-ifup: no bridge for guest interface found
Modified /etc/netplan yaml file as per man pages:
QEMU lauching with:
VM starts up and stops for
VM has no assigned IP address and thus no connection to the Internet.
Any advise highly appreciated!
1 Answer 1
So far you specified nic which means you created the virtual HW, but you have not yet connected it to anything.
Assuming you have setup a bridge for it already you need to tell qemu to connect to that.
But let me warn you, IIRC bridging onto wireless devices wasn’t always working great. It should have changed nowadays, but be aware that depending which doc/blog you read you might get outdated info.
That should help you resolve your setup issue, but I really want to mention that libvirt would do all that messing with qemu command-line and net prep for you? And if you hate XML files let uvtool do it for you. Or if you don’t like libvirt consider multipass which will also do all of that for you (but by default without libvirt).
Как избежать 5-минутной задержки загрузки в 18.04: «Запущено задание запуска для сетевых интерфейсов Raise»
Проблема: 5 минутная задержка при запуске
Устройство: плата UP (небольшая плата x86), работающая 18.04, с беспроводным USB-адаптером Panda PAU05, подключенным через HDMI к монитору
Конфигурация сети: с использованием netplan и systemd-networkd. NETworkManager не установлен.
Когда Ethernet подключен, устройство загружается быстро. Я могу отключить Ethernet и положиться на Wi-Fi. SSH работает и т. Д.
Я возился с моим планом, чтобы сделать интерфейсы Ethernet и Wi-Fi необязательными, но это не помогает. Я также попытался удалить интерфейс Ethernet, но это не помогло. Вот /etc/netplan/config.yaml Я бегу сейчас:
Изменить: я вижу несколько похожих вопросов, но я не вижу ответа, который использует netplan. Это ошибка / отсутствующая функция в netplan?
Редактировать: исправлены отступы и комментарии в config.yaml. (Я скопировал и вставил, затем отредактировал ssid и pw.)
Thread: A start job is running for raise network interfaces (5 mins 1 sec) in ubuntu16.04
Thread Tools
Display
A start job is running for raise network interfaces (5 mins 1 sec) in ubuntu16.04
i have installed ubuntu 16.04 in my laptop.
starting ubuntu is fast when i have LAN cabled connected.
when LAN cable disconnected then it is taking around 5 minutes to get login screen.
it was showing this message with timer on screen at that long time.
«A start job is running for raise network interfaces (2 minutes of 5 mins 1 sec)»
1) how can i skip this delay (5 mins for waiting network).
like if there are some shortcut keys which i typed then the startup script should not wait for 5 mins, it should directly skip the network interface checking and go to login screen.
or
2) how can i permanently stop network interface check only when LAN cable not connected.
Re: A start job is running for raise network interfaces (5 mins 1 sec) in ubuntu16.04
The system is set up to make a wired connection to the router and to do that automatically. But is cannot complete the task because the ethernet cable is disconnected. So, it tries again and again until finally some part of the OS gets the message.
There should be an icon on the top panel for the Network Manager. With the cable connected the icon will be two arrows going in the opposite direction. With the cable disconnected the icon will look like an upside down cone. Click on the icon; select Edit Connections; Select Wired Connection; Click Edit; Go to the General tab and untick the box labelled «Automatically connect to this network when it is available.»
In future when you want to make a wired connection to the router, then Click on the Network Manager icon and untick & re-tick Enable Networking. That should prompt Network Manager to start making the wired connection to the router.
It is a machine. It is more stupid than we are. It will not stop us from doing stupid things.
Ubuntu user #33,200. Linux user #530,530
Why is ssh too slow when I access in Ubuntu 18.04?
I’ve recently installed Ubuntu 18.04 and set the network and I configured NIS client to get user information from the server.
The problem is when I access this server through ssh, it is too slow to get a shell from the server. I’ve been digging out to solve this problem and found this error message from /var/log/auth.log but I don’t know how to do that. What should I do?
1 Answer 1
This problem is induced by the network interface, netplan, which is newly adapted in Ubuntu 18.04. Usually, when users configure this interface, they put optional: true attribute in the *.yaml to set an ethernet like below.
The reason why they put that attr is because if there is no attr in the file, it will hang in a certain amount of time on boot showing the message.
But the problem is that when you put this attr, an optional instruction in /etc/pam.d/common-session runs and this makes an error while you are trying to make a connection to the server
So, you need to comment out to get rid of time out while making a connection or session with the server.
A start job is running for eth0
I am using a new installation of Arch Linux and whenever I boot my system I have to wait for 90 seconds as there is a start job running for my network interfaces.
I installed Arch yesterday and whenever I do ip a I get that ethernet interfaces is in DOWN state. I used a wired usb tether to complete the whole installation. I just want to remove that start job process while starting. I saw a solution somewhere in Arch community that I have to disable my interface using:
I haven’t done that yet. My question is if I disable that interface will that cause any problems in future? I am not using any LAN connections now. Will that cause any problems if in future I want to use a LAN or some kind of ethernet connection?
Output of find /etc/systemd :
Startup finished in 5.369s (firmware) + 1.785s (loader) + 5.214s (kernel) + 1min 33.882s (userspace) = 1min 46.252s graphical.target reached after 1min 33.882s in userspace
Output of systemd-analyze :
Output of systemd-analyze critical-analyze :
Output of systemd-analyze blame :
Output of systemctl status dhcpcd@eth0.service and dhcpcd@enp1s0f1 :
I recently disabled enp1s0f1. That might be the reason it is disabled.
3 Answers 3
I’d say it’s very likely the problem you’re seeing is with the dhcpcd@eth0.service that’s configured on your system. So my recommendation would be to disable it, hopefully that’s enough to make that timeout during boot disappear:
I’ll go over the evidence to support that claim. There’s more troubleshooting that can be done here, I’ll suggest some more steps (in case you want to look further, or troubleshoot similar issues in the future.)
The main evidence of the issue is the message on output of systemctl status dhcpcd@eth0 which says:
Failed with result «dependency» means, in this case, it was waiting for something else, that failed. This service will have a dependency on eth0.device and this device will not appear, so that’s the probable source of the timeout. You can take a look at systemctl status eth0.device to see if anything else shows up, it’s possible it will (but then, it’s possible it won’t.)
Like you mentioned in your question, there’s probably a mix up between eth0 and the actual device name of enp1s0f1 in your system. systemd (more specifically udevd) will rename network interfaces to give them a consistent name and this typically happens very early at boot (sometimes even before systemd comes up), so systemd will not really see the eth0 name anymore.
If you want to enable DHCP on that interface in the future, enable dhcpcd@enp1s0f1 instead.
The output of systemd-analyze critical-chain supports the hypothesis of timeout on that dhcpcd@eth0 service, which you can see from these two steps:
The times after @ are the clock times right after boot. The wpa_supplicant service came up 13s after systemd started, but network.target was only reached at 1m33s (roughly the 90s you talk about.)
You would probably had seen dhcpcd@eth0 here more explicitly, but the unit actually went into the «loaded»/»inactive» state, rather than «failed», so that’s probably why it isn’t listed prominently here (and in systemd-analyze blame ), which would have helped point it out as the culprit.
Finally, one step that’s usually a great start when troubleshooting systemd boot issues is to start by looking at the bare systemctl status output, which will tell you whether the system is in «degraded» state, which indicates that something failed during boot. You want to ensure the system status will be «running», so investigating those failures will typically uncover issues such as timeouts, etc.
Hopefully these tips will be helpful to you in digging deeper and understanding what is happening in your system. Also hoping that disabling that dhcpcd@eth0 is enough to solve the boot delay you’re experiencing.
«waiting for network configuration» Problem
This problem happens sometimes when ubuntu starts up. You can’t really boot to the interface sometimes.
Splash Screen with the 5 dots and a message saying:
waiting for network configuration
waiting an additional 60 seconds for network configuration
6 Answers 6
If you are typing this from LXTerminal while logged in to the GUI then:
Remove whatever written there and just keep this:
It is very good idea to keep a backup copy of «interfaces» file just in case so please make sure to save a «interfaces.bak» file before you do anything
Ctrl + O if you are using nano and Ctrl + S (File > Save) if you are using leafpad.
Ctrl + X if you are using nano and Ctrl + Q (File > Quit) if you are using leafpad.
In every situation that I have run into this it is a problem in /etc/network/interfaces
You should not have to remove everything as suggested in an earlier post, but rather inspect for common problems.
In my case it was defining the gateway parameter for additional ethernet IPS. You only need to define the gateway for the primary interface for each card.
What I mean by this is if your file looks like this:
The 2nd gateway param will cause ubuntu to hang for 60+ secs during boot, you only need to define the gateway for the first eth0 section, you DO need to define the gateway for any additional nic cards, IE eth1, wlan0 etc but NOT for additional IPS assigned to the same nic. Earlier version of Ubuntu did not have any issues with this, but Ubuntu 12.04 does not like it. Be nice if it could simply ignore it.
I’m sure there are other «problems» in this file that can cause this, so you should inspect the file and make sure there are no typos etc.
Basically you edit this /etc/init/failsafe.conf file and disable (comment) the sleep commands which actually pause the system. Besides accomplishing the job, at least in my case there was no error at all in the network configuration, so everything went fine.
By the way, you solution only allows to configure the loopback interface, something I could not afford in my setup (I had to manually setup the interfaces and bridges).
The real(!) solution to this problem is following command:
Warning: After this change a permanently connected interface might stay down after boot until systemd receives a real plug event. See Notes below.
Example before (look at auto eth0 ):
Example after (look at allow-hotplug eth0 ):
If the interfaces are in auto mode, you express: «These interfaces are crucial for boot, so we must wait for them to come up before we have booted.» Hence, if they do not come up, Ubuntu delays the boot with failsafe, waiting for them to appear for up to 120 seconds. And this is the right thing to do.
In contrast, Interfaces which are set to allow-hotplug tell Ubuntu, that they are optional. Hence they are not essential to boot.
Ubuntu records which interfaces are available at install time, and assumes, that they are important for later operation. This is a conservative choice, in case the interface is later needed because some Service binds to it, as such services fail to start if they miss the interface being up.
There also is a kernel setting which allows processes to bind to nonexistent IPs, so you can always use allow-hotplug if you like, without harming the stability of the boot process. However, this is a completely different story.
Notes (update 2018-01-04):
After upgrading one of my systems to Debian Stretch and switching to SystemD, boot became unbearably delayed while waiting for the (permanently connected outside) interface br0 to come up. However with allow-hotplug the interface br0 stayed down after boot. Perhaps this is caused by SystemD not receiving any real or synthetic plug event on such an interface. I did not dig deeper into this, as some obscure crontab entry @reboot /sbin/ifup br0 for root fixed it for me. (This works, but probably is something, which better should not be recommended to others. I’d like to hear if somebody has some better idea.)
((Text ends here, the rest is for your entertainment))
And here is a bed time story, inspired by this:
Some crops farmers went on rampage. Their crops dried out! So they investigated why there was not enough water in the irrigation ditch. In the nearer distcance they immediately spotted their culprit. The dam! The damned dam held up all the water!
From this moment on it was clear what to do. «Blow up the dam!» they yelled and started to collect their dynamite. Then they all headed straight for the dam.
The little son of one of the farmers asked his father about what was going on. He told his son: «There’s not enough water in the ditch, so we blow up the dam!» Then he immediately left to follow the pack.
«But», the little one tried to shout after his father, «But there is a valve! Just open the valve!» Sadly, his voice was too gentle, and his legs were too short, so this message did not reach anybody.
The boy sat down and cried. Half an hour later he heared the distant «Boom» which destroyed his favorite plaground at the dam, where the valve was located, too.
What happened next?
The Flood swept away all the precious crops. The bank took away the boy’s father’s farm. His father was unable to pay for a good school. So the boy joined the army to get a higher education. There he learned everything about the phyics of explosives and now tries to invent a blast resitant dam.
What has this story to do with this here?
Arch Linux
You are not logged in.
#1 2014-10-29 07:00:35
[SOLVED] A start job is running for udev wait for Complete Device I.
Since recently boot hangs 1 min and 3s on the message:
A start job is running for udev wait for Complete Device Initialization (..s / 3min)
After 40s, this message is shortly interrupted by the message:
Starting Trigger Flushing of Journal to Persistent Storage.
[ OK ] Started Trigger Flushing of Journal to Persistent Storage.
The problem doesn’t happen on every boot, but on about 4 of 5 boots.
Has anyone a hint on how to debug this?
Edit
I found something which may match to the 1 minute waiting gap (between 08:03:01 and 08:04:02; 4th to 5th line):
So maybe it’s something with the iwlwifi?
Edit 2:
this 1:01min gap between
Edit 3:
Last edited by Carl Karl (2014-11-02 09:42:45)
#2 2014-10-29 16:50:26
Re: [SOLVED] A start job is running for udev wait for Complete Device I.
By running systemd-analyze blame I found out systemd-udev-settle.service is responsible for that delay. After reading in the internets that that service is not necessary if no LVM are used, I tried to disable that service which didn’t worked.
So I masked it instead:
and now booting is fast again, the 1m3s delay is gone.
But I’m still not sure whether this is a clean solution, so if you have better knowledge about this, please let me know.
#3 2014-10-29 19:43:46
Re: [SOLVED] A start job is running for udev wait for Complete Device I.
For the past 3 days, I have been suffering from an identical problem but only on my laptop (Intel CPU, 1 ssd). Not sure what triggered it. Often these kinds of problems seem to follow an update although I have not yet tracked down the guilty package (if any).
#4 2014-10-29 21:46:10
Re: [SOLVED] A start job is running for udev wait for Complete Device I.
laptop (Intel CPU, 1 ssd).
Same configuration here. And good to know I’m not the only one, thanks for your answer.
#5 2014-10-29 22:07:40
Re: [SOLVED] A start job is running for udev wait for Complete Device I.
Same here, Intel + ssd. Thanks for the fix/workaround. It solves the boot delay issue.
#6 2014-11-02 09:18:19
Re: [SOLVED] A start job is running for udev wait for Complete Device I.
Same problem here since systemd update 216-3. My configuration is in my sig.
Thanks for the fix. I’d mark the thread as solved, masking a service is not a bad workaround.
Outstanding IIAB issues (network & Node-RED) on Ubuntu Server 19.04 [released 2019-04-18] #1586
Comments
holta commented Mar 29, 2019 •
@jvonau @floydianslips «A start job is running for Wait for Network to be Configured» holds up boot (for more than 2 min) every time, on BIG-sized IIAB install on Ubuntu Server 19.04 Beta, in a VM.
Likely affects MIN-sized & MEDIUM-sized too?
What are the best ways to diagnose this?
@m-anish «systemctl start nodered» fails every time on Ubuntu 19.04 Beta:
Mar 29 00:49:53 box.lan systemd[1]: nodered.service: Service RestartSec=100ms expired, scheduling restart.
Mar 29 00:49:53 box.lan systemd[1]: nodered.service: Scheduled restart job, restart counter is at 5.
Mar 29 00:49:53 box.lan systemd[1]: Stopped Node-RED.
Mar 29 00:49:53 box.lan systemd[1]: nodered.service: Start request repeated too quickly.
Mar 29 00:49:53 box.lan systemd[1]: nodered.service: Failed with result ‘exit-code’.
Mar 29 00:49:53 box.lan systemd[1]: Failed to start Node-RED.
Verify that nodejs & npm hopefully install cleanly on their own as part BIG-sized IIAB install on Ubuntu 19.04 upon it’s final release 2019-04-18. Until then, this manual workaround is (likely) necessary, e.g. during early April 2019: https://github.com/iiab/iiab/blob/master/roles/nodejs/tasks/main.yml#L74-L76
MySQL database password-changing failure during fresh install of IIAB on Ubuntu 19.04, when using sudo to install IIAB, as per the official http://download.iiab.io instructions:
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
Thread: Ubuntu 18.04 beta2 server installer unable to config network on 16.04 kvm host
Thread Tools
Display
Ubuntu 18.04 beta2 server installer unable to config network on 16.04 kvm host
I am trying to install Ubuntu 18.04 server on Ubuntu 16.04 kvm host.
I am using ubuntu-18.04-beta2-live-server-amd64.iso
1. At text mode, «Timed out waiting for device dev-disk-by. device.» «Dependency failed for /subiquity_config.» warnings appear.
2. Installer pause at «A start job is running for Wait for Network to be Configured» for nearly 2 mins.
3. In «Network connection», the progress bar stop at 66%, and then show a «Network configuration timed out; please verify your settings». In network setting I use «Used DHCPv4 on this interface» and «Do not use (IPv6)». In fact, my ISP does not support IPv6. Anyway, the installer does not work here.
— Tried fresh install 17.04, everything run nice.
— Tried fresh install 17.10, the installer run ok. However after installation, it show «A start job is running for Wait for Network to be Configured» for a long time when boot, and unable to connect to network after that.
— Tried fresh install 17.04, then upgrade to 17.10. Everything seems perfect. No warning, no pause, able to connect to network.
I guess that is the problem of netplan, but I am not sure.
Re: Ubuntu 18.04 beta2 server installer unable to config network on 16.04 kvm host
I have just discover ubuntu-18.04-beta2-server-amd64.iso and install 18.04 successfully.
However, after installation, the system is still unable to connect to network.
Then I try remove netplan and install ifupdown, then my system works.
So I quite sure the problem come from netplan.
Debian 10 cloud-init waiting for DHCP on boot with static network configuration
Problem is that boot is delayed by waiting for DHCP, although I have a valid network configuration and it’s applied after this delay.
What can I do to skip this delay?
I can provide more info if needed. Thanks.
3 Answers 3
Seems a network config is applied from a template ( /etc/network/cloud-interfaces-template ) before the cloud-init configuration is written.
You can test that this template is the culprit by changing the cloud-image before first start:
(patching the image as changing network config in e.g. bootcmd is too late.)
I still need to find a way to apply this change or prevent the use of this template with cloud-init though.
I met the same problem.
Here is a better way to resolve it, just set DHCP timeout to a shorter time.
Then this image can function correctly in NoCloud environment or DHCP network.
Great pointers by @zany
In my case I was trying to configure a Debian 11 generic cloud image with cloud-init and a static IP on my KVM host (using dmacvicar libvirt Terraform provider)
My network-config file was:
Then I was surprised that during VM creation, the interface was requesting a DHCP lease ( journalctl is your friend) before cloud-init config would actually kick in and configure the interface as per my static settings (exacltly like the OP described)
Unfortunatelly disabling the intial dhcp request happens before cloud-init kicks in, so really no easy way to prevent dhclient wasting a precious minute or so trying to get an offer that will never come.
What I was able to accomplish though, was fixing DNS resolution by using the following bootcmd: block in my user-data
In the above commands, I’m bringing the interface down which stops the dormant dhclient process, then I’m removing the interface definition file that initially sets ens3 in dhcp mode, and finally I’m bringing the ens3 interface back up, which applies what’s set in /etc/network/interfaces.d/50-cloud-init.cfg like a champ.
With that, the subsequent cloud-init stages in the initial boot process were now able to fully reach the internet by name. That was critical for the later stages such the packages: block to succeed, since it needed DNS working to resolve the apt repo server name.
Here’s the more detailed user-data excerpt:
Despite not being on Debian10, the issue sounded so familiar that thought I’d share my experience in case you face this issue in newer releases.
A start job is running for Raise network interfaces
Включаю компьютер с Ubuntu, ввожу пароль для расшифровки раздела и система начинает пять минут ждать таймаута, выдавая надпись из темы, только после чего она включается. Сети вроде тоже не появляется, но она и не нужна.
Как убрать таймаут?
Та же проблема. debian 9.
При запуске A start job is running for Raise network interfaces и таймер в 5 минут.
При выключении/перезагрузке было похожее сообщение об ошибке с сетевыми драйверами и таймер в 15 минут.
Причем, если не подождать даже 10 секунд и сделать хардрезет, то под виндой потом вайфай карта определяется, но работать отказывается, пока не загрузится дебиан и не выключится почеловечески.
Подключал non-free, ставил оттуда чтото, пробовал драйвера с офсайта производителя, что-то из этого помогло, 15-минутный таймер при выключении пропал. Но при старте все еще «А start job is running for Raise network interfaces»
На моей девятке этого нет, в отличие от Ubuntu (которая, кстати, с момента установки себя так вела).
Дело было не то, что б очень давно, но все равно подробностей установки не помню уже. Кажется, в процессе установки, еще в деб-инсталлере все было ок, находило обе сетевых и без проблем подключалось к вай-фай. А сразу после установки ни один из интерфейсов не поднимался, и для проводной карты это решилось (барабанная дробь) переименованием проводного интерфейса в то, что система пыталась искать вместо стандартного eth0.
вайфай карта определяется, но работать отказывается,
«Холодное» выключение должно помогать, в «мозгах» вафли остается «linux-версия микрокода», т.е. какие-то специфичные опции для работы linux-драйвера.
Сначала надо найти проблему, в чем затык, т.к. это не ответ:
переименованием проводного интерфейса
Какие глупые настройки в NM, ведь у тебя он из коробки был?
Я меня был net-install образ 9ки.
в процессе установки, еще в деб-инсталлере все было ок, находило обе сетевых и без проблем подключалось к вай-фай. А сразу после установки ни один из интерфейсов не поднимался
Соответственно, на момент сразу после установки, я имел консоль без ДЕ и отсутствие интернета. Про наличие нетворк менеджера ничего не скажу, почему то был уверен, что он ставится только вместе с ДЕ.
Порывшись в телефоне нашел это:
Ахтунг! Фотки экрана! ШОК-КОНТЕНТ 18+!
Это, видимо, до переименования. Или сразу же после. http://savepic.net/9386973.htm
А это после того, как переименовал eth0 и проводной интернет завелся. Сразу после первого обновления пакетов: http://savepic.net/9400285.htm
Дальше, после установки КДЕ, вайфай завелся через стандартный конекшен эдитор из трея, а проводным с тех пор не пользовался.
Дальше, когда мне надоело ждать по 20 минут при каждой перезагрузке (15 при выключении и еще 5 на старте), я пробовал ставить что-то из non-free, еще что-то с сайта риалтека и 15-минутный тайм-аут пропал.
в /etc/apt/sources.list до сих пор вот так:
А фиг знает почему так было, сустемд любит всякую хрень ждать по полчаса, надо было тогда смотреть. Если щас всё нормально, то и фиг пока с ним.
Благодарю, действительно помогло убрать таймер и при загрузке тоже.
Failed to start wait for network to be configured, network interface failed
I have installed OMV5 on a raspberry pi 3b + and after rebooting while loading the following message appears
After this I enter username and password and check the configuration of the raspberry. I run the ifconfig command and I get this:
I run the ipaddress command to see the address of the raspberry and nothing appears to me
I have read in the forum that executing the following commands was solved but in my case I remain the same
sudo rm /etc/systemd/network/99-default.link
sudo omv-salt deploy run systemd-networkd
If someone could help me, why can’t I find the solution
I have exactly the same issue.
Same for me with Raspberry 4B.
Fixed it by myself.
OMV5 changes the network setting of the system. Fortunately these settings can be configured with the commandline tool omv-firstaid, which comes with omv.
Had the same issue and could fix it thanks to your explanation.
Hi, I have the same issue. I found if I remove DHCP reservation on router, it works. But if I put back my reservation, service will fail on boot. Where is old IP (used on installation) cached and how to wipe this cache? Or how to fix this?
RPi 4b: OMV + Docker: Adguard, Home Assistant
Fixed it by myself.
OMV5 changes the network setting of the system. Fortunately these settings can be configured with the commandline tool omv-firstaid, which comes with omv.
Thanks Peter. This helped.
When I installed the OMV V 5.x on Raspberry pi based on an article on internet, it was all working fine. However, last weekend, I tried to update raspberry pi OS using «update» and «upgrade» command from command line (using putty). And since then, the rpi lost connectivity to network. It wasn’t showing on the router as a connected device. I was worried and was thinking of reinstalling the OMV 5 from scratch. I was a bit reluctant as I had all my drives mounted and shares created and mapped etc. etc. and didn’t want to go through the pain.
But then came across your article. From the list of above steps, I ran thru 1-4 (except 3) and on omv-firstaid utility, I configured the Ethernet and the Wifi interfaces. Rebooted after that and «magic» 
«waiting for network configuration» Problem
This problem happens sometimes when ubuntu starts up. You can’t really boot to the interface sometimes.
Splash Screen with the 5 dots and a message saying:
waiting for network configuration
waiting an additional 60 seconds for network configuration
6 Answers 6
If you are typing this from LXTerminal while logged in to the GUI then:
Remove whatever written there and just keep this:
It is very good idea to keep a backup copy of «interfaces» file just in case so please make sure to save a «interfaces.bak» file before you do anything
Ctrl + O if you are using nano and Ctrl + S (File > Save) if you are using leafpad.
Ctrl + X if you are using nano and Ctrl + Q (File > Quit) if you are using leafpad.
In every situation that I have run into this it is a problem in /etc/network/interfaces
You should not have to remove everything as suggested in an earlier post, but rather inspect for common problems.
In my case it was defining the gateway parameter for additional ethernet IPS. You only need to define the gateway for the primary interface for each card.
What I mean by this is if your file looks like this:
The 2nd gateway param will cause ubuntu to hang for 60+ secs during boot, you only need to define the gateway for the first eth0 section, you DO need to define the gateway for any additional nic cards, IE eth1, wlan0 etc but NOT for additional IPS assigned to the same nic. Earlier version of Ubuntu did not have any issues with this, but Ubuntu 12.04 does not like it. Be nice if it could simply ignore it.
I’m sure there are other «problems» in this file that can cause this, so you should inspect the file and make sure there are no typos etc.
Basically you edit this /etc/init/failsafe.conf file and disable (comment) the sleep commands which actually pause the system. Besides accomplishing the job, at least in my case there was no error at all in the network configuration, so everything went fine.
By the way, you solution only allows to configure the loopback interface, something I could not afford in my setup (I had to manually setup the interfaces and bridges).
The real(!) solution to this problem is following command:
Warning: After this change a permanently connected interface might stay down after boot until systemd receives a real plug event. See Notes below.
Example before (look at auto eth0 ):
Example after (look at allow-hotplug eth0 ):
If the interfaces are in auto mode, you express: «These interfaces are crucial for boot, so we must wait for them to come up before we have booted.» Hence, if they do not come up, Ubuntu delays the boot with failsafe, waiting for them to appear for up to 120 seconds. And this is the right thing to do.
In contrast, Interfaces which are set to allow-hotplug tell Ubuntu, that they are optional. Hence they are not essential to boot.
Ubuntu records which interfaces are available at install time, and assumes, that they are important for later operation. This is a conservative choice, in case the interface is later needed because some Service binds to it, as such services fail to start if they miss the interface being up.
There also is a kernel setting which allows processes to bind to nonexistent IPs, so you can always use allow-hotplug if you like, without harming the stability of the boot process. However, this is a completely different story.
Notes (update 2018-01-04):
After upgrading one of my systems to Debian Stretch and switching to SystemD, boot became unbearably delayed while waiting for the (permanently connected outside) interface br0 to come up. However with allow-hotplug the interface br0 stayed down after boot. Perhaps this is caused by SystemD not receiving any real or synthetic plug event on such an interface. I did not dig deeper into this, as some obscure crontab entry @reboot /sbin/ifup br0 for root fixed it for me. (This works, but probably is something, which better should not be recommended to others. I’d like to hear if somebody has some better idea.)
((Text ends here, the rest is for your entertainment))
And here is a bed time story, inspired by this:
Some crops farmers went on rampage. Their crops dried out! So they investigated why there was not enough water in the irrigation ditch. In the nearer distcance they immediately spotted their culprit. The dam! The damned dam held up all the water!
From this moment on it was clear what to do. «Blow up the dam!» they yelled and started to collect their dynamite. Then they all headed straight for the dam.
The little son of one of the farmers asked his father about what was going on. He told his son: «There’s not enough water in the ditch, so we blow up the dam!» Then he immediately left to follow the pack.
«But», the little one tried to shout after his father, «But there is a valve! Just open the valve!» Sadly, his voice was too gentle, and his legs were too short, so this message did not reach anybody.
The boy sat down and cried. Half an hour later he heared the distant «Boom» which destroyed his favorite plaground at the dam, where the valve was located, too.
What happened next?
The Flood swept away all the precious crops. The bank took away the boy’s father’s farm. His father was unable to pay for a good school. So the boy joined the army to get a higher education. There he learned everything about the phyics of explosives and now tries to invent a blast resitant dam.
What has this story to do with this here?
Start job is running for wait for network to be configured. Ubuntu server 18.04
I am receiving the message «Start job is running for wait for netowrk to be configured» during bootup. Computer hangs for 2 minutes until whatever is going on times out. Network connection appears to be there since there appears to be a successful synchronization to time ntp.ubuntu.com just prior to the hang.
This is within VirtualBox, after setting Adapter 1 to NAT, Adapter 2 to Host-Only Adapter, and setting /etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml as follows:
(I’m new to netplan; admittedly I’m poking in the dark here).
Reviewing syslog after bootup, here is what I see:
I find it curious the timestamp doesn’t reflect the 2 minute wait, but perhaps that’s another question.
and tried disabling systemd-networkd-wait-online.service as indicated but that does not appear to work (still get the 2 minute wait).
Any ideas what’s going on here, and how to fix it?
A start job is running for wait for network to be configured
Running a recently built server rig on 18.04.04 with a Gigabyte Aorus Z490 AX motherboard. I’ve had nothing but trouble with networking compatibility between this motherboard and 18.04 from the start. I cannot reliably raise the wired ethernet connection on reboot without performing a hard restart and only plugging in the ethernet cable to the back after the startup sequence is finished.
Every time during bootup sequence, I see:
[FAILED] Failed to start Raise network interfaces.
see systemctl status networking.service for details.
and. «a start job is running for Wait for Network to be Configured» which takes a full two minutes.
Here are the results of ‘systemctl status networking.service’
Jul 19 21:57:50 server systemd[1]: Starting Raise network interfaces.
Jul 19 21:57:50 server ifup[1107]: Missing required variable: address
Jul 19 21:57:50 server ifup[1107]: Missing required configuration variables for interface enp4s0/inet.
Jul 19 21:57:50 server ifup[1107]: Failed to bring up enp4s0.
Jul 19 21:57:50 server systemd[1]: networking.service: Main process exited, code=exited, status=1/FAILURE
Jul 19 21:57:50 server systemd[1]: networking.service: Failed with result ‘exit-code’.
Jul 19 21:57:50 server systemd[1]: Failed to start Raise network interfaces.
Using their NVMEUpdate utility has gotten me exactly nowhere.
WARNING: To avoid damage to your device, do not stop the update or reboot or power off the system during this update.
Inventory in progress. Please wait [|. ]
Num Description Ver.(hex) DevId S:B Status
=== ================================== ============ ===== ====== ==============
01) Intel(R) Ethernet Controller (2) 1.69(1.45) 15F3 00:004 Update not
I225-V available
Tool execution completed with the following status: Device not found.
Press any key to exit.
Ideas as to how I get this done and make this machine raise the network interface automatically on all reboots?
ifupdown was deprecated in 17.10.
cat /etc/netplan/config.yaml
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
enp4s0:
addresses: [ 192.168.1.2/24 ]
gateway4: 192.168.1.1
nameservers:
addresses: [ 208.67.222.222, 208.67.220.220 ]
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
enp4s0:
addresses: [ 192.168.1.2/24 ]
gateway4: 192.168.1.1
nameservers:
addresses: [ 208.67.222.222, 208.67.220.220 ]
All the extra spaces where none should be «might» be messing with you. Example of modified config:
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
enp4s0:
dhcp4: false
dhcp6: false
addresses: [192.168.1.2/24]
gateway4: 192.168.1.1
nameservers:
addresses: [208.67.222.222,208.67.220.220]
What is the output of this command?
I don’t see anything wrong that jumps out to me. Don’t know if disabling dhcp is required or not. I always do.
+1 on disable the wireless, this may cause further heartburn.
+1 on having a clean netplan file. I think I would check this out first.
All the extra spaces where none should be «might» be messing with you. Example of modified config:
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
enp4s0:
dhcp4: false
dhcp6: false
addresses: [192.168.1.2/24]
gateway4: 192.168.1.1
nameservers:
addresses: [208.67.222.222,208.67.220.220]
What is the output of this command?
Because I have some kind of driver/kernel module compatibility issue, I’m certain this won’t fix my ultimate problem with raising network interfaces automatically on every reboot, but I appreciate the help on refining this Netplan config.
WARNING: To avoid damage to your device, do not stop the update or reboot or power off the system during this update.
Inventory in progress. Please wait [|. ]
Num Description Ver.(hex) DevId S:B Status
=== ================================== ============ ===== ====== ==============
01) Intel(R) Ethernet Controller (2) 1.69(1.45) 15F3 00:004 Update not
I225-V available
Tool execution completed with the following status: Device not found.
Press any key to exit.
What am I missing here? I have re-flashed one MoBo BIOS update so far (one update later than factory setting). For now, all I am relying on is waiting for a combo of more BIOS updates from Gigabyte and the release of 18.04.5 in August.
WARNING: To avoid damage to your device, do not stop the update or reboot or power off the system during this update.
Inventory in progress. Please wait [|. ]
Num Description Ver.(hex) DevId S:B Status
=== ================================== ============ ===== ====== ==============
01) Intel(R) Ethernet Controller (2) 1.69(1.45) 15F3 00:004 Update not
I225-V available
Tool execution completed with the following status: Device not found.
Press any key to exit.
What am I missing here? I have re-flashed one MoBo BIOS update so far (one update later than factory setting). For now, all I am relying on is waiting for a combo of more BIOS updates from Gigabyte and the release of 18.04.5 in August.
If Desktop versions are working, then I’d check that the driver used is the same between the desktop and server installs.
Also, Desktops use network-manager (usually) to handle all network settings. You can try to use nmcli and see if that matters. I’d be surprised if it does, but anything is possible.
I still could not get the rig to auto-raise network interfaces on startup. In fact I couldn’t even get it online at all. ‘ifconfig’ did show a change in the Ethernet interfaces, and I attempted to alter netplan to reflect this. However I got nowhere, and had to remove the new NIC device for now, to at least get this server rig connected again, albeit with its problems raising network interfaces unless plugging in the Ethernet cable after the full boot process, and following a hard shutdown.
No matter what, the boot sequence would still show
«Failed to start raise network interfaces»
Jul 27 20:44:42 server systemd[1]: Starting resolvconf-pull-resolved.service.
Jul 27 20:44:42 server systemd[1]: Started resolvconf-pull-resolved.service.
While the new NIC device was still installed, it would give me this messages:
[FAILED] Failed to start resolvconf-pull-resolved.service.
See ‘systemctl status resolvconf-pull-resolved.service’ for details.
Here are those results. Inactive/dead
Okay n00b question here, but does ifup/ifdown have any relevance here?
ifup/ifdown were deprecated as user commands pre-18.04, but they are still used in the systemd Unit file for networking on 20.04. I don’t have any 18.04 systems and we will be skipping that LTS, it appears.
On a server, the resolver doesn’t need to be complex. I purge systemd-resolved and resolvconf from my system and manually edit the /etc/resolv.conf file to point at the DNS I wish to use. I have internal DNS that does caching, so having a local cache on each system really isn’t needed (regardless of what Canonical thinks). Many consumer routers will provide DNS caching too.
Where DNS resolving becomes more complex is with laptops and other portable devices. Fortunately, only 1 of my systems is considered «portable» and that one uses DoH already.
But starting at the first steps is where I’d begin.
Driver loaded?
Driver used?
Card Up manually?
Card Up automatically?
Only then would I deal with DNS issues. People confuse DNS problems with network and routing problems all the time. They are not the same and need completely different troubleshooting. To tell whether an issue is DNS or driver+device or router, the simple ping command should be used.
Ping by IP, in this order:
local router (192.168.x.x)
1.1.1.1
What does the output mean?
There are different error messages based on whether the DNS lookup happened and worked correctly or not.
If DNS doesn’t seem to be working, disable resolvconf and systemd-resolved using typical commands. sudoedit the /etc/resolv.conf file and put
Of course, a minimal knowledge of IPv4 networking is needed to better understand the different messages.
The first error way above says this:
Missing required variable: address
Did that get fixed by the netplan suggestions above?
When posting, please show the command and all output unless it gets over a page long together. Here’s mine on a 20.04 box:
Jul 26 10:14:21 regulus systemd[1]: Starting Raise network interfaces.
Jul 26 10:14:22 regulus systemd[1]: Finished Raise network interfaces.
Odd to see Docs: man:interfaces(5), since the interfaces file was deprecated and mine is empty. 20.04 uses netplan. My working netplan file is exactly:
$ more 01-ens3-static.yaml
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
ens3:
addresses:
— 172.22.22.3/24
dhcp4: false
dhcp6: false
gateway4: 172.22.22.1
nameservers:
addresses: [ «172.22.22.80»,»172.22.22.81″ ]
So people don’t get confused. THIS IT NOT THE OP’s information. Data in this post is shown only as an example.
Fu, thanks for the additional advice.
Turned out that although the machine was saying that it ‘Failed to raise network interfaces’ on all startups,’ after installing PCI device network interface controller, the device was thankfully recognized by Ubuntu Server 18 due to its older and well-tested driver/module (so I assume).
It was in fact able to ping both the router and external IPs such as 1.1.1.1 and 8.8.8.8 (and anything else) despite saying ‘Failed to raise network interfaces’ when the ethernet cable was plugged into the NIC from the start.
Eventually, this whole problem worked itself out (as long as I keep using the newly-installed NIC, by way of adjusting the iptables and netplan settings to reflect the new eth0 address/name. The addition of the network interface controller changed the eth0 interface name from ‘enp4s0’ to two separate eth0 interfaces called ‘enp1s0’ and ‘enp5s0.’
Installed new NIC device
Deleted /etc/network/interfaces.d/setup (some problem interfering with /etc/network/interfaces settings. This stopped «Failed to start Raise network interfaces» even before correcting Netplan and IPtables to reflect eth0 changes.
The extra network interface (NIC device) now shows ‘enp1s0’ and ‘enp5s0’ instead of just ‘enp4s0.’ Adjusted Netplan and ipconfig.rules.v4 settings to refer to ‘enp1s0.’ This allows successful raising of network interfaces and all connectivity available on startup.
Because I’m just insane and OCD enough to stress out about making the original motherboard’s Intel ethernet controller work just as well, I am awaiting further updates from Ubuntu (18.04.5 as of July 2020) and further BIOS updates to the Gigabyte Aorus Z490 Pro AX motherboard. I’ve had no success working directly with these hardware modules/drivers to fix the problem, until the devs roll out updates. Is this thinking correct? As it stands now, something still is completely bugged up and wrong with one or the other, it seems.
If this is solved by the new NIC, please use the «Thread Tools» button to mark it that way. At some point, the i225-v will have great support, so I’d check every few months. Put a reminder on your calendar. OTOH, if you don’t have 2.5Gbps switch or router, then that NIC isn’t all that useful, yet.
Thanks, I’ll look at that link. I can’t tell what the Gbps specs are for the router (Google Fiber Network Box GFRG200); I know max speeds in and out from the Internet are about 1000 Mbps. So stressing out over it will be a waste of time, I assume?
Thanks, I’ll look at that link. I can’t tell what the Gbps specs are for the router (Google Fiber Network Box GFRG200); I know max speeds in and out from the Internet are about 1000 Mbps. So stressing out over it will be a waste of time, I assume?
If you only have 1 computer at home, then the WAN connection speeds are the most important limiting factor, but if you have multiple devices and want those networked and able to talk to each other, then usually faster is better.
Why use 10base-tx if 100base-tx is available cheap?
Why use 100base-tx if 1000base-tx is available cheap?
Why use 1000base-tx if 2500 or 10Kbase-tx is available and cheap?
My home network has multiple subnets and about 20 systems. Most traffic is within my LANs, not over the internet. My internet connection is about 30 Mbps / 5 Mbps. That’s plenty fast. I remember running a business on a 128 Kbps ISDN connection, so 5 Mbps up is huge!
Thread: A start job is running for wait on all «auto»
Thread Tools
Display
A start job is running for wait on all «auto»
Upon startup of my Ubuntu 15.04 Server, my boot is stopped by the message:
This lasts for about 2 minutes and 10 seconds. I also just finished installing DRBL. The server is not meant to connect to the internet.
If anyone has a way to disable or find the cause for this, I would be very grateful.
Here is my interfaces file:
Re: A start job is running for wait on all «auto»
Re: A start job is running for wait on all «auto»
Thanks, but it seems to be working with the strange IP config. I don’t even really remember why I set up the interfaces file like that. I previously tried to change the /etc/failsafe file but that didn’t effect this. I’ll try to reboot when I get a chance and see if it gives me the same message.
Re: A start job is running for wait on all «auto»
Having 2 interfaces with a single IP on the same subnet is an error.
The eth0:0 stanza isn’t helping at all. Best to remove it.
Re: A start job is running for wait on all «auto»
Thanks for the recommendation! However, we have yet to see if this stops the waiting problem. I’ll post back here when I can access the machine Monday morning.
Re: A start job is running for wait on all «auto»
Well that seems to have solved it, thanks for the help!
Howto migrate from networking to systemd-networkd with dynamic failover
Systemd’s systemd-networkd can be used to replace the existing networking system on Raspbian.
How does it work with Raspbian on a Raspberry Pi with two interfaces for ethernet and wlan? Can I also realize dynamic failover for them?
2 Answers 2
It will not work with Raspbian Stretch!
Here you will find the last tested revision for Raspbian Stretch Lite.
♦ Abstract
networkd is a small and lean service to configure network interfaces, designed mostly for server use cases in a world with hotplugged and virtualized networking. Its configuration is similar in spirit and abstraction level to ifupdown, but you don’t need any extra packages to configure bridges, bonds, vlan etc. It is not very suitable for managing WLANs yet; NetworkManager is still much more appropriate for such Desktop use cases. [1]
♦ Step 1: Preparation
I will have attention to a headless installation only with ssh. If you are using this, double check typos or so otherwise you are lost with a broken connection. If you want a headless installation then look at SSH (Secure Shell) and follow section 3. Enable SSH on a headless Raspberry Pi (add file to SD card on another machine).
Disable the old stuff. Don’t stop any service, only disable them! So it will take effect only on next boot. How to do it just follow to
♦ Step 2: Setup the wired ethernet interface (eth0)
♦ Step 3: Setup wlan interface (wlan0)
Reboot and good luck 😉
It is possible that the RasPi gets a new ip addresses so you may have to look at it for the next connection with ssh.
♦ Step 4: Bonding wired and wifi interface for failover
First disable the single ethernet and wifi network files:
Then setup bonding with these four files:
If finished that, it’s time to reboot.
It is possible that the RasPi gets a new ip address so you may have to look at it for the next connection with ssh.
Then you can check the bonding status:
Test bonding: with the bonding status above you will see that the Currently Active Slave: will change and the MII Status: is down.
If your are headless, don’t down both interfaces together 😉
Be patient after setting wlan0 up. I may take some time to reconnect to the router and manage bonding. This time ssh will not response.
For a more in-depth review of bonding you may have a look at Dynamic network failover prioritize wifi over ethernet.
Why is ssh too slow when I access in Ubuntu 18.04?
I’ve recently installed Ubuntu 18.04 and set the network and I configured NIS client to get user information from the server.
The problem is when I access this server through ssh, it is too slow to get a shell from the server. I’ve been digging out to solve this problem and found this error message from /var/log/auth.log but I don’t know how to do that. What should I do?
1 Answer 1
This problem is induced by the network interface, netplan, which is newly adapted in Ubuntu 18.04. Usually, when users configure this interface, they put optional: true attribute in the *.yaml to set an ethernet like below.
The reason why they put that attr is because if there is no attr in the file, it will hang in a certain amount of time on boot showing the message.
But the problem is that when you put this attr, an optional instruction in /etc/pam.d/common-session runs and this makes an error while you are trying to make a connection to the server
So, you need to comment out to get rid of time out while making a connection or session with the server.
What does NetworkManager-wait-online.service do?
NetworkManager-wait-online.service fails at boot and it delays my startup
4 Answers 4
Some code runs off the network
In some multi-user environments part of the boot-up process can come from the network. For this case systemd defaults to waiting for the network to come on-line before certain steps are taken.
Majority of Desktop Users
Unlike some multi-user environments most Ubuntu desktop users have the Operating System and drivers on their hard disks, SSDs or Live Boot USBs.
There is a glitch where some users wait an extremely long time for network to come up during boot. In this case the recommendations is to set the maximum wait time to 30 seconds. A better way is to simply disable the service at boot time.
For many users 10 to 15 seconds can be sliced off the parallel boot time by using:
After you sign on you will likely get a message bubble stating you’ve now been connected to the network (WiFi or Ethernet access to Internet).
It appears that this service simply waits, doing absolutely nothing, until the network is connected, and when this happens, it changes its state so that other services that depend on the network can be launched to start doing their thing.
So, it appears that this service is absolutely benign, it does not waste any time during boot, and it actually constitutes an optimization, so you are only going to make things worse if you disable it.
(Services that need the network will start before the network is up, at a time when many other services are also starting up and contention is high, and these services will be unable to do anything useful, so they will just keep retrying to connect to the network, until the network finally comes up.)
«waiting for network configuration» Problem
This problem happens sometimes when ubuntu starts up. You can’t really boot to the interface sometimes.
Splash Screen with the 5 dots and a message saying:
waiting for network configuration
waiting an additional 60 seconds for network configuration
6 Answers 6
If you are typing this from LXTerminal while logged in to the GUI then:
Remove whatever written there and just keep this:
It is very good idea to keep a backup copy of «interfaces» file just in case so please make sure to save a «interfaces.bak» file before you do anything
Ctrl + O if you are using nano and Ctrl + S (File > Save) if you are using leafpad.
Ctrl + X if you are using nano and Ctrl + Q (File > Quit) if you are using leafpad.
In every situation that I have run into this it is a problem in /etc/network/interfaces
You should not have to remove everything as suggested in an earlier post, but rather inspect for common problems.
In my case it was defining the gateway parameter for additional ethernet IPS. You only need to define the gateway for the primary interface for each card.
What I mean by this is if your file looks like this:
The 2nd gateway param will cause ubuntu to hang for 60+ secs during boot, you only need to define the gateway for the first eth0 section, you DO need to define the gateway for any additional nic cards, IE eth1, wlan0 etc but NOT for additional IPS assigned to the same nic. Earlier version of Ubuntu did not have any issues with this, but Ubuntu 12.04 does not like it. Be nice if it could simply ignore it.
I’m sure there are other «problems» in this file that can cause this, so you should inspect the file and make sure there are no typos etc.
Basically you edit this /etc/init/failsafe.conf file and disable (comment) the sleep commands which actually pause the system. Besides accomplishing the job, at least in my case there was no error at all in the network configuration, so everything went fine.
By the way, you solution only allows to configure the loopback interface, something I could not afford in my setup (I had to manually setup the interfaces and bridges).
The real(!) solution to this problem is following command:
Warning: After this change a permanently connected interface might stay down after boot until systemd receives a real plug event. See Notes below.
Example before (look at auto eth0 ):
Example after (look at allow-hotplug eth0 ):
If the interfaces are in auto mode, you express: «These interfaces are crucial for boot, so we must wait for them to come up before we have booted.» Hence, if they do not come up, Ubuntu delays the boot with failsafe, waiting for them to appear for up to 120 seconds. And this is the right thing to do.
In contrast, Interfaces which are set to allow-hotplug tell Ubuntu, that they are optional. Hence they are not essential to boot.
Ubuntu records which interfaces are available at install time, and assumes, that they are important for later operation. This is a conservative choice, in case the interface is later needed because some Service binds to it, as such services fail to start if they miss the interface being up.
There also is a kernel setting which allows processes to bind to nonexistent IPs, so you can always use allow-hotplug if you like, without harming the stability of the boot process. However, this is a completely different story.
Notes (update 2018-01-04):
After upgrading one of my systems to Debian Stretch and switching to SystemD, boot became unbearably delayed while waiting for the (permanently connected outside) interface br0 to come up. However with allow-hotplug the interface br0 stayed down after boot. Perhaps this is caused by SystemD not receiving any real or synthetic plug event on such an interface. I did not dig deeper into this, as some obscure crontab entry @reboot /sbin/ifup br0 for root fixed it for me. (This works, but probably is something, which better should not be recommended to others. I’d like to hear if somebody has some better idea.)
((Text ends here, the rest is for your entertainment))
And here is a bed time story, inspired by this:
Some crops farmers went on rampage. Their crops dried out! So they investigated why there was not enough water in the irrigation ditch. In the nearer distcance they immediately spotted their culprit. The dam! The damned dam held up all the water!
From this moment on it was clear what to do. «Blow up the dam!» they yelled and started to collect their dynamite. Then they all headed straight for the dam.
The little son of one of the farmers asked his father about what was going on. He told his son: «There’s not enough water in the ditch, so we blow up the dam!» Then he immediately left to follow the pack.
«But», the little one tried to shout after his father, «But there is a valve! Just open the valve!» Sadly, his voice was too gentle, and his legs were too short, so this message did not reach anybody.
The boy sat down and cried. Half an hour later he heared the distant «Boom» which destroyed his favorite plaground at the dam, where the valve was located, too.
What happened next?
The Flood swept away all the precious crops. The bank took away the boy’s father’s farm. His father was unable to pay for a good school. So the boy joined the army to get a higher education. There he learned everything about the phyics of explosives and now tries to invent a blast resitant dam.
What has this story to do with this here?
«waiting for network configuration» Problem
This problem happens sometimes when ubuntu starts up. You can’t really boot to the interface sometimes.
Splash Screen with the 5 dots and a message saying:
waiting for network configuration
waiting an additional 60 seconds for network configuration
6 Answers 6
If you are typing this from LXTerminal while logged in to the GUI then:
Remove whatever written there and just keep this:
It is very good idea to keep a backup copy of «interfaces» file just in case so please make sure to save a «interfaces.bak» file before you do anything
Ctrl + O if you are using nano and Ctrl + S (File > Save) if you are using leafpad.
Ctrl + X if you are using nano and Ctrl + Q (File > Quit) if you are using leafpad.
In every situation that I have run into this it is a problem in /etc/network/interfaces
You should not have to remove everything as suggested in an earlier post, but rather inspect for common problems.
In my case it was defining the gateway parameter for additional ethernet IPS. You only need to define the gateway for the primary interface for each card.
What I mean by this is if your file looks like this:
The 2nd gateway param will cause ubuntu to hang for 60+ secs during boot, you only need to define the gateway for the first eth0 section, you DO need to define the gateway for any additional nic cards, IE eth1, wlan0 etc but NOT for additional IPS assigned to the same nic. Earlier version of Ubuntu did not have any issues with this, but Ubuntu 12.04 does not like it. Be nice if it could simply ignore it.
I’m sure there are other «problems» in this file that can cause this, so you should inspect the file and make sure there are no typos etc.
Basically you edit this /etc/init/failsafe.conf file and disable (comment) the sleep commands which actually pause the system. Besides accomplishing the job, at least in my case there was no error at all in the network configuration, so everything went fine.
By the way, you solution only allows to configure the loopback interface, something I could not afford in my setup (I had to manually setup the interfaces and bridges).
The real(!) solution to this problem is following command:
Warning: After this change a permanently connected interface might stay down after boot until systemd receives a real plug event. See Notes below.
Example before (look at auto eth0 ):
Example after (look at allow-hotplug eth0 ):
If the interfaces are in auto mode, you express: «These interfaces are crucial for boot, so we must wait for them to come up before we have booted.» Hence, if they do not come up, Ubuntu delays the boot with failsafe, waiting for them to appear for up to 120 seconds. And this is the right thing to do.
In contrast, Interfaces which are set to allow-hotplug tell Ubuntu, that they are optional. Hence they are not essential to boot.
Ubuntu records which interfaces are available at install time, and assumes, that they are important for later operation. This is a conservative choice, in case the interface is later needed because some Service binds to it, as such services fail to start if they miss the interface being up.
There also is a kernel setting which allows processes to bind to nonexistent IPs, so you can always use allow-hotplug if you like, without harming the stability of the boot process. However, this is a completely different story.
Notes (update 2018-01-04):
After upgrading one of my systems to Debian Stretch and switching to SystemD, boot became unbearably delayed while waiting for the (permanently connected outside) interface br0 to come up. However with allow-hotplug the interface br0 stayed down after boot. Perhaps this is caused by SystemD not receiving any real or synthetic plug event on such an interface. I did not dig deeper into this, as some obscure crontab entry @reboot /sbin/ifup br0 for root fixed it for me. (This works, but probably is something, which better should not be recommended to others. I’d like to hear if somebody has some better idea.)
((Text ends here, the rest is for your entertainment))
And here is a bed time story, inspired by this:
Some crops farmers went on rampage. Their crops dried out! So they investigated why there was not enough water in the irrigation ditch. In the nearer distcance they immediately spotted their culprit. The dam! The damned dam held up all the water!
From this moment on it was clear what to do. «Blow up the dam!» they yelled and started to collect their dynamite. Then they all headed straight for the dam.
The little son of one of the farmers asked his father about what was going on. He told his son: «There’s not enough water in the ditch, so we blow up the dam!» Then he immediately left to follow the pack.
«But», the little one tried to shout after his father, «But there is a valve! Just open the valve!» Sadly, his voice was too gentle, and his legs were too short, so this message did not reach anybody.
The boy sat down and cried. Half an hour later he heared the distant «Boom» which destroyed his favorite plaground at the dam, where the valve was located, too.
What happened next?
The Flood swept away all the precious crops. The bank took away the boy’s father’s farm. His father was unable to pay for a good school. So the boy joined the army to get a higher education. There he learned everything about the phyics of explosives and now tries to invent a blast resitant dam.
What has this story to do with this here?
Mentions having to delete the swap partition and creating it again.
I can try to do this with Gparted but my main concern is losing my current set up in Ubuntu as I’m not entirely sure what will happen if I mess with swap as suggested in the thread. Anyone able to help?
15 Answers 15
A start job is running for dev-disk-by.
followed by a 90 second delay during each boot, complete the following steps:
Install GParted using the Software Center
Open GParted and see what partitions Ubuntu is currently using
Edit the fstab file using the line below.
If you have a device that you are not currently using, insert a # and a space at the beginning of that line comment it out.
Reboot and the start job shouldn’t appear again.
I had the same issue after resizing my primary partition on my VM since gparted live forced me to delete & reinitialize my swap to do so. That caused a new UUID to be set that didn’t match the fstab file.
To avoid the issue, in /etc/fstab you can either
Replace the swap UUID with the new one (run sudo blkid to find it) after the primary partition resizing.
Or, comment out the swap partition before (or after) the primary partition resizing.
I would recommend the former since it is the way the OS is meant to be setup.
Looks like the issue was due to the fact that even though fstab had an entry for a swap, there actually wasn’t one. I used GParted to resize the partition and created a new Swap. I then copied the UUID into the fstab file.
Main Situation :
You need to check the UUID under those files (answered in details on other answers. )
This could be caused by udev if you have a rule script under /etc/udev/rules.d/ that is not meant to run at boot time, if the script fail it will make that fstab step go on forever, just edit your script to match your needs or delete it.
Crypted partitions can be confusing because the main partition have an UUID and the mapped Decrypted one have an other UUID different from the main one for a single partition they have to be defined in different place etc/crypttab and /etc/fstab
Real UUID need to be specified in etc/crypttab
Virtual UUID need to be at /etc/fstab
A device that is setup to be mounted at boot time but is not present in the system or detached like an usb drive.
After upgrading to 20.04 LTS, network now takes 2 minutes to start because of cloud-init
Further digging shows:
/etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/ contains some files that are 4+ years old:
Are the files in /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d supposed to be removed or updated at some point?
This textbox defaults to using Markdown to format your answer.
You can type !ref in this text area to quickly search our full set of tutorials, documentation & marketplace offerings and insert the link!
These answers are provided by our Community. If you find them useful, show some love by clicking the heart. If you run into issues leave a comment, or add your own answer to help others.
Want to learn more? Join the DigitalOcean Community!
Join our DigitalOcean community of over a million developers for free! Get help and share knowledge in Q&A, subscribe to topics of interest, and get courses and tools that will help you grow as a developer and scale your project or business.
Arch Linux
You are not logged in.
#1 2016-06-04 15:14:58
[*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
When I booted my computer today and had no ethernet connection, I got this error:
[*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0 (14 s / 1min 30s).
I was a especially confused as I never had this problem before. It just connected via the ethernet connection if it was plugged in and otherwise not. I’m not sure if I enabled the dhcpcd service myself or if it is on by default when installing Arch Linux. In any case, I disabled it, and I enabled it again with:
But I still get the same message when booting the computer. Everything works fine if the ethernet cable is plugged in. As far as I understood, the dhcpcd client should just start as soon as the state of enp2s0f0 link is UP?
So actually, what I want is to have a ethernet connection as soon as I plug in an ethernet cable, but it should not block my booting process. How can I do that?
#2 2016-06-04 15:22:41
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
same here, apparently caused by latest systemd update to 230-3
Arch is home!
cwm rofi weaver clifm vis lizzy pass terminator
https://github.com/Docbroke
#3 2016-06-04 15:47:09
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
You’re absolutely right! I just downgraded to version 229 of systemd and I had the problem no longer.
I’m quite new to Arch, someone knows how/where to report this problem?
#4 2016-06-04 15:49:31
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
Ah, I just saw there are already some bugs reported in the bug tracker which are related to systemd: https://bugs.archlinux.org/. But I’m not sure if this specific bug has been reported.
Last edited by fabianbl (2016-06-04 16:04:51)
#5 2016-06-05 00:26:24
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
https://git.archlinux.org/svntogit/pack … aa4257a02f
First commit for the arch packaging of systemd 230 2016-05-22 10:08:52 (GMT)
https://bugs.archlinux.org/index/proj1? … &sort=desc
Last bug report against systemd was opened on 2016-5-14 20:55 (GMT)
So the last bug report was before was packaged for arch.
So if there is a bug in 230 no one has filed a bug report about it.
OffTopic:
Took over an hour generating a url string for that bug report query that fluxbb would accept and still generated a valid url.
Edit:
Amended bugtracker url to show closed bugs as well. The change does not appear to affect findings.
Last edited by loqs (2016-06-05 00:49:32)
#6 2016-06-05 00:42:24
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
Install wicd and wicd-gtk. Disable dhcpcd, and enable wicd?
#7 2016-06-05 03:44:45
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
I had that too for my wireless. The name of my wireless changed from the update. Just had to disable the old name and enable the new name.
#8 2016-06-05 09:15:37
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
Hardly the same here (I think I don’t have to open a new thread):
It occurs with systemd-230, not with 229. Occurs during the boot, but after that, I’ve got internet. I use ethernet and static ip, no dhcp, and I still have the issue (but as I’ve said, despite this I’ve got internet after booting):
All boots fine until it reaches:
Then, after having to wait for 1min 30 s, where it should appear [ OK ] in green in the left appears a word in yellow that I’m not fast enough to read (I think that word is DEMAND, but I’m still not sure) and the boot process continues without problems.
The dmesg output is this:
I’ve tried to disable ipv6 in /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/all/disable_ipv6 and /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/enp2s0/disable_ipv6 without results, so the use of ipv6 does not seem to be the problem.
What drives me mad is that I get the same output with systemd-229. The first output says that enp2s0 is down and not ready, but the next message says that is up and that link becomes ready. So, which «start job» is running for sys-subsystem-net-devices-eth0.device that does not finish, makes me wait for 1min 30s, and not even finish in that time but after it all I’ve got internet anyway. With systemd-230, because systemd-229 get over it, I do not have to wait and I still have internet.
Last edited by josealb77 (2016-06-05 09:27:18)
#9 2016-06-05 16:07:32
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
This seems to be not only for the interfaces that are not used, but even those that are. I’m getting this on my wireless now. I get the «start job» message but it only waits until the wireless can be connected.
It seems the network.target is no longer being brought up in parallel with other targets, but now it is a hard dependency of user-sessions and multi-user targets:
#10 2016-06-05 21:28:47
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
I have the same problem with dhcpcd on my workstation. Everything is the same as with systemd 229. The only exception is a delay for about 10s with the same message as described in the topic.
#11 2016-06-05 22:15:00
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
At a very rough look of commits touching files in the units directory this https://github.com/systemd/systemd/comm … e247557770 seems as though it might be able to cause the issue.
Only examined by inspection not tried reverting it.
Edit:
Setting /usr/lib/systemd/system/systemd-user-sessions.service /etc/systemd/system/systemd-user-sessions.service to
Seems to work ( the simpler drop in version did not work as dependency was being removed )
@loqs, the suggested file already exists (with systemd 230-3), and is no different than what you have posted
Copied the original rather than modified version thanks to Docbroke for pointing that out. Corrected to now be the modified version.
Should also have been /etc/systemd/system/systemd-user-sessions.service not /usr/lib/systemd/system/systemd-user-sessions.service
Last edited by loqs (2016-06-06 02:33:44)
#12 2016-06-06 01:37:28
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
@loqs, the suggested file already exists (with systemd 230-3), and is no different than what you have posted
EDIT: just checked the link you posted, and it seems that «After = network.target», needs to be removed, that solves the issue.
Last edited by Docbroke (2016-06-06 01:50:03)
Arch is home!
cwm rofi weaver clifm vis lizzy pass terminator
https://github.com/Docbroke
#13 2016-06-06 07:10:22
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
PERFECT!! That worked for me!!
#14 2016-06-06 08:44:15
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
I was almost ready to start searching the issue regarding the dhcpcd 
#15 2016-06-16 03:53:24
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
still present with systemd 230-4
#16 2016-06-16 04:17:20
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
still present with systemd 230-4
And have you disabled the requisite service?
Registered Linux User #482438
Online
#17 2016-06-16 04:25:06
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
still present with systemd 230-4
And have you disabled the requisite service?
Well, of course I did. I most deffinitely did. I mean, I did it just now, removing «network.target». That does indeed fix the issue 🙂
#18 2016-06-18 18:21:05
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
I have had the same problem and read this thread with the idea of trying to fix it. However, in post #11 «/etc/systemd/system/systemd-user-sessions.service» is mentioned. Is this a text file? I don’t have it there and find finds an executable file elsewhere. Where am I going wrong in my thinking and how do deal with this problem? I’m a real newbie here and a slightly extend reply would be appreciated.
Also, just as learning item, several posts mention such things as «systemd 230-3» or «systemd 230-4». How does one get such specific information?
#19 2016-06-18 21:49:57
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
I have had the same problem and read this thread with the idea of trying to fix it. However, in post #11 «/etc/systemd/system/systemd-user-sessions.service» is mentioned. Is this a text file? I don’t have it there and find finds an executable file elsewhere. Where am I going wrong in my thinking and how do deal with this problem? I’m a real newbie here and a slightly extend reply would be appreciated.
Also, just as learning item, several posts mention such things as «systemd 230-3» or «systemd 230-4». How does one get such specific information?
Your terminal can give you the info:
#20 2016-06-18 21:57:32
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
Your terminal can give you the info:
Registered Linux User #482438
Online
#21 2016-06-19 00:12:08
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
Thank you! Simple things like that are sometimes hard to find in a search.
#22 2016-06-21 23:03:35
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
I’m still not getting how to fix this issue though. What service shoud I disable and how? (and can I really disable it safely?) Is `/etc/systemd/system/systemd-user-sessions.service` a file I need to create, since it doesn’t exist on my setup? Or should I rather wait for the next version of systemd to bring a fix?
#23 2016-06-22 00:01:23
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
I’m still not getting how to fix this issue though. What service shoud I disable and how?
See post #11 in this thread the issue here is a dependency upstream added for network.target
(and can I really disable it safely?)
See the committ message from the link in post #11 that documents why the change was made. Removing the dependancy will allow that issue to occurr.
Is `/etc/systemd/system/systemd-user-sessions.service` a file I need to create, since it doesn’t exist on my setup?
See UNIT FILE LOAD PATH section of man 5 systemd.unit. /etc/systemd/system/systemd-user-sessions.service is being used to override the shipped unit file /usr/lib/systemd/system/systemd-user-sessions.service
Or should I rather wait for the next version of systemd to bring a fix?
What is your source for upstream reverting to the old behavior?
#24 2016-06-22 19:31:55
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
Or should I rather wait for the next version of systemd to bring a fix?
What is your source for upstream reverting to the old behavior?
I wasn’t speaking under that assumption. I was rather assuming that a future package update might somehow fix the issue without having to override systemd’s default configuration, which looks like a temporary workaround to me. So, should I apply the fix you’ve suggested in post #11 right now, or should I expect Arch packagers to patch the issue in the foreseeable future? (not that I badly need my SSH sessions to end cleanly, but I would rather keep my system tweaks to a minimum amount, unless there is no cleaner way.)
#25 2016-06-22 19:53:55
Re: [*** ] A start job is running for dhcpcd on enp2s0f0.
Or should I rather wait for the next version of systemd to bring a fix?
What is your source for upstream reverting to the old behavior?
I wasn’t speaking under that assumption. I was rather assuming that a future package update might somehow fix the issue without having to override systemd’s default configuration, which looks like a temporary workaround to me. So, should I apply the fix you’ve suggested in post #11 right now, or should I expect Arch packagers to patch the issue in the foreseeable future? (not that I badly need my SSH sessions to end cleanly, but I would rather keep my system tweaks to a minimum amount, unless there is no cleaner way.)
Arch in general does not apply patches that have not been accepted upstream. Looking at https://github.com/systemd/systemd/blob … service.in no change has occurred since the comitt that introduced this issue.
Looking at https://github.com/systemd/systemd/issues it does not seem to have been reported upstream.
I can not speak for others but I did not report this upstream because:
1) It may only be an issue with certain network managers ( reports seem limited to using netctl and dhcpcd
2) This appears to be an intentional change ( perhaps unknowingly breaking netctl and dhcpdp based services ) and I can not see it being resolved without an alternative solution to having networking only shutdown after user sessions.
Given that I can not estimate if or when the old behavior would be restored.
Edit:
Appears to reported here ( filed against dhcpcd https://bugs.archlinux.org/task/49685 )
Last edited by loqs (2016-06-24 15:22:16)
Fixed: a start job is running for sys-subsystem-net-devices-eth0.device
When booting up, my Arch Linux virtual machine always tells me that “a start job is running for sys-subsystem-net-devices-eth0.device” and I have to wait for another 1 minute and 30s, which is very annoying.
How did I solve this problem?
Once Arch Linux is booted up, open up a terminal window and check system log with the following command:
And here’s what I found.
As you can see from the output, [email protected] is waiting for eth0 interface which has failed.
The systemctl status [email protected] command tells me that this service is supposed to automatically start with system boot.
And if I run ip address show command in the terminal, I know that enp0s3 interface has already obtained an IP address from my home router.
So there’s really no need to get eth0 interface up. All I need to do is to disable [email protected]
The annoying “a start job is running for sys-subsystem-net-devices-eth0.device” message will be gone and 1 minute and 30s is saved every time Arch Linux virtual machine is booted up.
Later on I found that I have changed the network mode from the default NAT mode to Bridged Adapter mode in Virtualbox. So the default eth0 interface won’t work in my Arch Linux virtual machine.
I hope this tutorial helped you solve the above problem. As always, if you found this post useful, then please subscribe to our free newsletter or follow us on Google+, Twitter or like our Facebook page. Thanks for visiting!
«waiting for network configuration» Problem
This problem happens sometimes when ubuntu starts up. You can’t really boot to the interface sometimes.
Splash Screen with the 5 dots and a message saying:
waiting for network configuration
waiting an additional 60 seconds for network configuration
6 Answers 6
If you are typing this from LXTerminal while logged in to the GUI then:
Remove whatever written there and just keep this:
It is very good idea to keep a backup copy of «interfaces» file just in case so please make sure to save a «interfaces.bak» file before you do anything
Ctrl + O if you are using nano and Ctrl + S (File > Save) if you are using leafpad.
Ctrl + X if you are using nano and Ctrl + Q (File > Quit) if you are using leafpad.
In every situation that I have run into this it is a problem in /etc/network/interfaces
You should not have to remove everything as suggested in an earlier post, but rather inspect for common problems.
In my case it was defining the gateway parameter for additional ethernet IPS. You only need to define the gateway for the primary interface for each card.
What I mean by this is if your file looks like this:
The 2nd gateway param will cause ubuntu to hang for 60+ secs during boot, you only need to define the gateway for the first eth0 section, you DO need to define the gateway for any additional nic cards, IE eth1, wlan0 etc but NOT for additional IPS assigned to the same nic. Earlier version of Ubuntu did not have any issues with this, but Ubuntu 12.04 does not like it. Be nice if it could simply ignore it.
I’m sure there are other «problems» in this file that can cause this, so you should inspect the file and make sure there are no typos etc.
Basically you edit this /etc/init/failsafe.conf file and disable (comment) the sleep commands which actually pause the system. Besides accomplishing the job, at least in my case there was no error at all in the network configuration, so everything went fine.
By the way, you solution only allows to configure the loopback interface, something I could not afford in my setup (I had to manually setup the interfaces and bridges).
The real(!) solution to this problem is following command:
Warning: After this change a permanently connected interface might stay down after boot until systemd receives a real plug event. See Notes below.
Example before (look at auto eth0 ):
Example after (look at allow-hotplug eth0 ):
If the interfaces are in auto mode, you express: «These interfaces are crucial for boot, so we must wait for them to come up before we have booted.» Hence, if they do not come up, Ubuntu delays the boot with failsafe, waiting for them to appear for up to 120 seconds. And this is the right thing to do.
In contrast, Interfaces which are set to allow-hotplug tell Ubuntu, that they are optional. Hence they are not essential to boot.
Ubuntu records which interfaces are available at install time, and assumes, that they are important for later operation. This is a conservative choice, in case the interface is later needed because some Service binds to it, as such services fail to start if they miss the interface being up.
There also is a kernel setting which allows processes to bind to nonexistent IPs, so you can always use allow-hotplug if you like, without harming the stability of the boot process. However, this is a completely different story.
Notes (update 2018-01-04):
After upgrading one of my systems to Debian Stretch and switching to SystemD, boot became unbearably delayed while waiting for the (permanently connected outside) interface br0 to come up. However with allow-hotplug the interface br0 stayed down after boot. Perhaps this is caused by SystemD not receiving any real or synthetic plug event on such an interface. I did not dig deeper into this, as some obscure crontab entry @reboot /sbin/ifup br0 for root fixed it for me. (This works, but probably is something, which better should not be recommended to others. I’d like to hear if somebody has some better idea.)
((Text ends here, the rest is for your entertainment))
And here is a bed time story, inspired by this:
Some crops farmers went on rampage. Their crops dried out! So they investigated why there was not enough water in the irrigation ditch. In the nearer distcance they immediately spotted their culprit. The dam! The damned dam held up all the water!
From this moment on it was clear what to do. «Blow up the dam!» they yelled and started to collect their dynamite. Then they all headed straight for the dam.
The little son of one of the farmers asked his father about what was going on. He told his son: «There’s not enough water in the ditch, so we blow up the dam!» Then he immediately left to follow the pack.
«But», the little one tried to shout after his father, «But there is a valve! Just open the valve!» Sadly, his voice was too gentle, and his legs were too short, so this message did not reach anybody.
The boy sat down and cried. Half an hour later he heared the distant «Boom» which destroyed his favorite plaground at the dam, where the valve was located, too.
What happened next?
The Flood swept away all the precious crops. The bank took away the boy’s father’s farm. His father was unable to pay for a good school. So the boy joined the army to get a higher education. There he learned everything about the phyics of explosives and now tries to invent a blast resitant dam.
What has this story to do with this here?
After upgrading to 20.04 LTS, network now takes 2 minutes to start because of cloud-init
Further digging shows:
/etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/ contains some files that are 4+ years old:
Are the files in /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d supposed to be removed or updated at some point?
This textbox defaults to using Markdown to format your answer.
You can type !ref in this text area to quickly search our full set of tutorials, documentation & marketplace offerings and insert the link!
These answers are provided by our Community. If you find them useful, show some love by clicking the heart. If you run into issues leave a comment, or add your own answer to help others.
Want to learn more? Join the DigitalOcean Community!
Join our DigitalOcean community of over a million developers for free! Get help and share knowledge in Q&A, subscribe to topics of interest, and get courses and tools that will help you grow as a developer and scale your project or business.
Thread: A start job is running for raise network interfaces (5 mins 1 sec) in ubuntu16.04
Thread Tools
Display
A start job is running for raise network interfaces (5 mins 1 sec) in ubuntu16.04
i have installed ubuntu 16.04 in my laptop.
starting ubuntu is fast when i have LAN cabled connected.
when LAN cable disconnected then it is taking around 5 minutes to get login screen.
it was showing this message with timer on screen at that long time.
«A start job is running for raise network interfaces (2 minutes of 5 mins 1 sec)»
1) how can i skip this delay (5 mins for waiting network).
like if there are some shortcut keys which i typed then the startup script should not wait for 5 mins, it should directly skip the network interface checking and go to login screen.
or
2) how can i permanently stop network interface check only when LAN cable not connected.
Re: A start job is running for raise network interfaces (5 mins 1 sec) in ubuntu16.04
The system is set up to make a wired connection to the router and to do that automatically. But is cannot complete the task because the ethernet cable is disconnected. So, it tries again and again until finally some part of the OS gets the message.
There should be an icon on the top panel for the Network Manager. With the cable connected the icon will be two arrows going in the opposite direction. With the cable disconnected the icon will look like an upside down cone. Click on the icon; select Edit Connections; Select Wired Connection; Click Edit; Go to the General tab and untick the box labelled «Automatically connect to this network when it is available.»
In future when you want to make a wired connection to the router, then Click on the Network Manager icon and untick & re-tick Enable Networking. That should prompt Network Manager to start making the wired connection to the router.
It is a machine. It is more stupid than we are. It will not stop us from doing stupid things.
Ubuntu user #33,200. Linux user #530,530
«Waiting for network configuration» adding 3 to 5 minutes to boot time
I get the following pieces of information at the startup, takes about 3 to 5 minutes, while normally about 1 minute:
I found after googling that I should change /etc/networks/interface. I commented out everything there but the problem remains:
How can you make the startup of Ubuntu 11.10 faster?
7 Answers 7
First off, this is a new behavior, documented in the 11.10 release notes, that I actually developed together with Scott Moser as an effort to make server boot more reliable.
Commenting out lo will mean you have no local network capability, which will break some programs when they try to use the network. It will also cause your system to never boot because it is so critical. So leave these two lines:
Keep in mind, there’s a known bug with VMware and dbus that also causes this message.
Virtual Machine (interface enp0s4) not assigned dynamic IPv4 address
bar17
Dabbler
I have a Ubuntu Server 20.04 virtual machine running on my FreeNAS 11.3-U5 box.
My problem is that my virtual Ubuntu Server is not being assigned an IP address.
I have an Edge Router X with Subnet 10.17.16.0/21 and gateway 10.17.17.4. The DHCP server runs on the Edge Router X.
I recently switched from a NetGear r7000 to my current Edge Router X (ERX) router and only use the r7000 as an AP with DHCP turned off. After years of reliable dd-wrt service it started having some weird problems. Since upgrading to the ERX, everything has been rock solid and all devices on my network have been assigned an IP by the Edge Router X DHCP server, except my virtual VM.
In the past, I had a problem with my virtual Ubuntu server on the FreeNAS. The problem and solution was to edit `/ etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml ` and change ` enp0s5 ` to ` enp0s4 ` as seen here «https://www.truenas.com/community/t. 04-server-in-vm-has-no-internet-access.75684/» @KrisBee had the solution. That problem had to do with removing a virtual CD ROM interface and the network interface #/position changing. It is not the current problem, but could be related somehow. Currently, the interface is assigned to the correct physical port and is using the ` VIRTIO ` interface.
Current /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml configuration:
I think there is something funny with the way that Ubuntu Server, FreeNAS, and the virtual NIC all interact.
As you can see, there is no IPv4 address on the virtual enp0s4 interface.
On boot there is an error message:
Searching this error gives suggestions to restart the networking service and/or edit the above mentioned yaml file by adding the line:
optional: true `. Neither of these work.
Running ip route returns nothing.
ip add 10.17.17.99 dev enp0s4
Adds inet 10.17.17.99/32 scope global enp0s4 to the enp0s4 interface.
ip route add 10.17.17.4 dev enp0s4 adds the route 10.17.17.4 dev enp0s4 scope link to the routing table (previously blank).
Neither of these together or separate fix the problem.
If I try the above commands with a subnet \21 it does not work.
The one relevant change I did do that coincides with this problem is that when I switched my routers I changed my network form 10.17.17.0 to 10.17.16.0 because to increase my IP range with the subnet \21 I had to otherwise my router said it was an invalid subnet. Perhaps the virtual machine somehow has the gateway or the subnet mask fixed and is not updating?
I would love to understand how to completely break down/disable/refresh the entire network interface and have the server request an IP from my router. I am not sure if this is a problem specific to the bhyve / freenas vm networking interface (like the above linked problem I had previously) or if it is more generic to linux ubuntu server networking.
HackWare.ru
Этичный хакинг и тестирование на проникновение, информационная безопасность
Решение проблемы: Live USB флэшка с Linux не загружается, ошибка «A start job is running for live-config contains the components that configure a live system during the boot process (late userspace)»
Debian является основой для многих дистрибутивов, поэтому если в самой Debian появляется какой-то баг, то он постепенно расползается сразу по нескольким дистрибутивам Linux.
Например, с ошибкой
Ещё признаками этой проблемы являются ошибки со словом nouveau:
Как можно заметить, прямо перед этими ошибками видна запись
В системах, где выводятся не все сообщения, загрузка может остановится именно на этой надписи, но к рассматриваемой проблеме она не имеет отношения.
Суть проблемы в том, что записанная Live система на USB флэшку или диск не загружается. Если дистрибутив показывает сообщения системного журнала о загрузке, то вы можете видеть приведённую выше ошибку.
Некоторые дистрибутивы настроены не выводить сообщения загрузки и используют экран заставки — в этом случае будет казаться, что система зависла на экране загрузки.
В этой статье я покажу как исправить проблему для Live дистрибутивов на USB флэшке.
На самом деле, проблема может возникнуть не только на Live системе, но и при обычной установке. Но в этом случае порядок действий другой — нужно загрузиться в систему (с помощью изменения опций загрузки, как показано ниже, либо переключиться в интерфейс командной строки), а затем обновить систему и/или установить видеодрайвер видеокарты для NVidia. Этот вариант для обычной установке Linux, не Live.
Что касается Live систем, то они не сохраняют сделанные на них изменений после перезагрузки, поэтому описанный выше метод не подходит. На самом деле, на Live системе тоже можно делать изменения, если система записана на USB диск. Для оптических дисков это невозможно в принципе.
Итак, приступим к исправлению проблемы!
Исправление ошибки A start job is running for live-config contains…
В меню загрузки нажмите е (или TAB). Откроется окно опций загрузки. Если в нём несколько строк, то передвиньте курсор на строку, которая начинается с
Посмотрите, встречаются ли в этой строке «quiet» и «splash»?
Я рекомендую убрать обе строки.
И, самое главное, добавьте в конец, через пробел, следующее:
Для продолжения загрузки нажмите F10 (или ENTER).
Если это сработает и система успешно загрузится, значит причина проблем с загрузкой в несовместимости драйверов с видеокартой NVidia.
Как изменить файлы в Live системе
Оптические диски с Live-системами привили привычку, что информацию на такой системе невозможно изменить. Дело, конечно, в ограничениях самих оптических дисков, а не режима Live.
В режиме Live на USB носителях разделы просто монтируются с параметром «только чтение». Поэтому достаточно перемонтировать раздел в режим записи и на нём будет возможно сохранить сделанные изменения.
Если вы исправляете проблему для Tails, то не забудьте при включении установить Пароль администратора.
Теперь нам нужно узнать имя диска, для этого введите команду:
На приведённом скриншоте, флэшка имеет имя /dev/sdb.
Теперь нужно определить, в какую точку файловой системы смонтированы разделы диска /dev/sdb. Все сделанные в системе монтирования выводит команда
Используя её в паре с grep можно ускорить поиск нужно информации (здесь и далее вместо /dev/sdb введите имя вашего диска):
Как видно на скриншоте, раздел /dev/sdb1 смонтирован в /lib/live/mount/medium. Также обращаем внимание на буквы ro, они означают «только для чтения».
Для перемонтирования раздела с разрешениями на запись, нужно выполнить команду вида:
Для моих данных это команда:
Опять делаю проверку:
Теперь нам нужно отредактировать конфигурационные файлы, из которых система считывает опции загрузки. Дистрибутивы Linux поддерживают загрузку в БИОС и в EFI — для каждого из этих вариантов свой конфигурационный файл. Дистрибутив может быть 32-битным или 64-битным — и вновь, для каждого из этих вариантов свой конфигурационный файл загрузки. То есть в общей сложности нам нужно будет отредактировать 4 файла.
Для Tails эти файлы расположены по следующим путям:
То есть искать нужно в точке монтирования (/lib/live/mount/medium/) директории syslinux и EFI/BOOT.
Открываем первые два файла:
Там перечислены все пункты меню, для Tails это:
Достаточно сделать изменения только для того пункта, которым вы пользуетесь. В случае Tails нужно изменить live.
Изменения нужно сделать такие же, как мы делали до этого в опциях загрузки, то есть нужно обязательно дописать:
И опционально можно удалить (я всегда удаляю, т. к. это сильно упрощает решение возникающих проблем) строки:
Когда всё готово, сохраняем и закрываем оба файла.
Открываем следующие два:
И повторяем сделанные изменения:
Также сохраните и закройте эти файлы.
Теперь попробуйте перезагрузиться. Больше не нужно редактировать параметры загрузки — система должна включиться нормально.
Cause a script to execute after networking has started?
I am relatively new to systemd and am learning its architecture.
Right now, I’m trying to figure out how to cause a custom shell script to run. This script needs to run after the networking layer has started up.
I’m running Arch, using systemd as well as netctl.
I then enabled the script with,
Upon restarting, the script does indeed run, but it runs prior to the network being started. In other words, the output in ip.txt displays no IPv4 address assigned to the primary interface. By the time I login, the IPv4 address has indeed been assigned and networking is up.
I’m guessing I could alter the point at which the script runs by messing with the WantedBy parameter, but I’m not sure how to do that.
Could someone point me in the right direction?
7 Answers 7
On systemd network configuration dependencies
It is very easy to affect systemd’s unit ordering. On the other hand you need to be careful about what a completed unit guarantees.
Configure your service
On current systems, ordering after network.target just guarantees that the network service has been started, not that there’s some actual configuration. You need to order after network-online.target and pull it in to achieve that.
For compatibility with older systems, you may need to order after network.target as well.
That’s for the unit file of your service and for systemd.
Implementation in current versions of software
Now you need to make sure that network-online.target works as expected (or that you at least can use network.target ).
The current version of NetworkManager offers the NetworkManager-wait-online.service which gets pulled in by network-online.target and thus by your service. This special service ensures that your service will wait until all connections configured to be started automatically succeed, fail, or time out.
The current version of systemd-networkd blocks your service until all devices are configured as requested. It is easier in that it currently only supports configurations that are applied at boot time (more specifically the startup time of `systemd-networkd.service).
For the sake of completeness, the /etc/init.d/network service in Fedora, as interpreted by the current versions of systemd, blocks network.target and thus indirectly blocks network-online.target and your service. It’s an example of a script based implementation.
If your implementation, whether daemon based or script based, behaves as one of the network management services above, it will delay the start of your service until network configuration is either successfully completed, failed for a good reason, or timed out after a reasonable time frame to complete.
You may want to check whether netctl works the same way and that information would be a valuable addition to this answer.
Implementations in older versions of software
Previously NetworkManager only guaranteed that at least one connection would get applied. And even for that to work, you would have to enable the NetworkManager-wait-online.service explicitly. This has been long fixed in Fedora but was only recently applied upstream.
Notes on network.target and network-online.target implementations
A daemon based network management service should also order itself before network.target even though it’s not very useful.
The package should install a symlink to the waiting service in the wants directory for network-online.target so that it gets pulled in by services that want to wait for configured network.
Related documentation
Final notes
I hope I not only helped to answer your question at the time you asked it, but also contributed to improving the situation in upstream and Linux distributions, so that I can now give a better answer than was possible at the time of writing the original one.
Debian. A start job is running for LSB: Raise Network Interfaces
Вечер добрый, ЛОР. Есть система с дебианом и такой проблемой, рандомно при загрузке стопорится на несколько минут с таким выхлопом. Что еще более странно, такие же сетевые карты на 2х других системах и там такой проблемы нет, везде стоит блоб firmware-realtek, но и без него было так же.
Фото:http://cs627317.vk.me/v627317609/2ca09/G30Q1hBTC7I.jpg
systemd-analyze critical-chain:
P.S. Доступ к системе ограничен, только ssh, буду благодарен за любую помощь
Он у тебя там не пытается автоматически интерфейс поднять и получить адреса по dhcp случаем?
Ну если проводным интерфейсом не пользуешься закомментируй строчки с eth0.
Как раз проводной и используется, он единственный. Гуглёж наводил на форум, где советовали закомментировать allow-hotplug, но результатом стало то, что интернет и вовсе пропал.
Ну это понятно, ты же интерфейс не поднимаешь =)
В общем костыльный вариант это прописать статику, но я бы просто запускал попозже этот инитскрипт или вообще бы отвязал от него остальные сервисы. С другой стороны тут я диванный, потому как с такими же параметрами у меня проблем нет (только systemd не используется)
Аналогичную картину вижу при загрузке, Debian 8.2, базовая установка, похожая картина в interfaces, стабильно по минуте висит пытаясь что-то там с сетью сделать, было б здорово решить. Кст иногда сеть так и не поднимает приходится руками ifup делать.
В сторону DHCP сервера. У вас интерфейс не поднимается.
На Дебиан тестинг была такая проблема. После очередного обновления systemd при отключенном сетевом проводе стало появляться это сообщение (при подключенном не было). Вылечилось комментированием строки allow-hotplug.
PS В пользу этой версии говорит и то, что «интернет пропал». При нормально функционирующей сети «iface eth0 inet dhcp» пропадать не должен в принципе.
a start job is running for udev wait for complete device initialization. Ubuntu Pi ARM #331
Comments
kingspeech64 commented Dec 10, 2019
After installing the driver boot hangs 2 minutes on the message:
a start job is running for udev wait for complete device initialization (Xmin Ys/ 2min 59s)
followed by ‘FAILED’
Debug is:
Did you read Troubleshooting most common issues? http://bit.ly/2Rofd0x [y/N] y
Distro: Ubuntu
Release: eoan
Kernel: 5.3.0-1014-raspi2
Driver version: 5.2.14
DisplayLink service status:
EVDI service version: 1.6.1
Vendor:
Subsystem:
VGA:
VGA (3D):
X11 version: 1.20.5+git20191008-0ubuntu1
X11 configs: /etc/X11/xorg.conf.d/20-displaylink.conf
File: /etc/X11/xorg.conf.d/20-displaylink.conf
Contents:
Section «OutputClass»
Identifier «DisplayLink»
MatchDriver «evdi»
Driver «modesetting»
Option «AccelMethod» «none»
EndSection
Providers: number : 1
Provider 0: id: 0x41 cap: 0x0 crtcs: 1 outputs: 1 associated providers: 0 name:modesetting
Use this information when submitting an issue (http://bit.ly/2GLDlpY)
Dec 10 14:58:54 ubuntu systemd[1]: displaylink-driver.service: Service RestartSec=5s expired, scheduling restart.
Dec 10 14:58:54 ubuntu systemd[1]: displaylink-driver.service: Scheduled restart job, restart counter is at 3137.
Dec 10 14:58:54 ubuntu systemd[1]: Stopped DisplayLink Driver Service.
Dec 10 14:58:54 ubuntu systemd[1]: Starting DisplayLink Driver Service.
Dec 10 14:58:54 ubuntu systemd[1]: Started DisplayLink Driver Service.
Dec 10 14:58:54 ubuntu systemd[17310]: displaylink-driver.service: Failed to execute command: Exec format error
Dec 10 14:58:54 ubuntu systemd[17310]: displaylink-driver.service: Failed at step EXEC spawning /opt/displaylink/DisplayLinkManager: Exec format error
Dec 10 14:58:54 ubuntu systemd[1]: displaylink-driver.service: Main process exited, code=exited, status=203/EXEC
Dec 10 14:58:54 ubuntu systemd[1]: displaylink-driver.service: Failed with result ‘exit-code’.
dash /opt/displaylink/DisplayLinkManager
/opt/displaylink/DisplayLinkManager: 6: Syntax error: word unexpected (expecting «)»)
file DisplayLinkManager
DisplayLinkManager: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (GNU/Linux), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=5720db8b7a6202d64b2e90a92716f0d0292a74ca, stripped
I conclude that this is an architecture error. The driver should be support ARM. Is there another way as cross compiling DisplayLinkManager to aarch64? It isn’t a permission problem. Also no bash/dash problem.
NOTE: I’m working with Raspberry Pi 4b with Ubuntu 19.10
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
How to successfully restart a network without reboot over SSH?
In Ubuntu 14.04 neither sudo service networking restart nor sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart do anything any more. They also both exit with code 1. Something has obviously changed (or half changed) but I can’t find what. This obviously causes problems with remote network reconfiguration and tools like Ansible.
What is the correct way to restart networking in Ubuntu 14.04 Server remotely?
5 Answers 5
Turns out this is a «feature». The only supported way of restarting an interface in Ubuntu Server is sudo ifdown eth0 && sudo ifup eth0
ifdown, ifup didn’t work for me (likely SSH connection timeout before the second command). What did work was:
This was on a 14.04 ubuntu-desktop system.
What’s changed is they don’t want you «bouncing» the network anymore. stopping, and starting, still work. restart no longer works. I just «solved» this «problem», that is to say I got the old behavior back. To revert to prior behavior: Take a 13.10 /etc/init/networking.conf file and replace the 14.04 file with it. (edit: clarified which replaces which)
The process looks like this:
Do the same for /etc/init.d/networking script, which is what the /etc/init/networking.conf file references/calls.
Obviously there’s a reason they put a defensive exit in there, but they don’t bother to really output what’s going on very well.
An entry does go into /var/log/upstart/networking.log when you try, that looks like:
But they really could/should have output that as the dialog message when you try service networking restart. ah well. figured it out and even a old-way work around.
EDIT: I have found this causes an unintentional triggering of the script controlled by /etc/init/failsafe.conf which is undesirable as it causes a 120 second timeout delay in every boot up. as well as perhaps masking actual misconfigurations/network issues which this delay’s appearance would indicate, but it’s already showing all the time. (e.g. An unplugged cable, which was allowing access to a network file share mapped in /etc/fstab, for instance)
In any case, I will figure out what is causing this always hitting the timeout, and post a fix when I find it.
after dist-upgrade «A start job is running for lsb: raise network interface» @boot #111
Comments
RafaelKa commented Oct 2, 2015
I installed http://mirror.igorpecovnik.com/Armbian_4.4_Bananapi_Debian_jessie_4.2.2.zip and runned apt-get dist-upgrade and now boots my BPI not anymore and halts on «A start job is running for lsb: raise network interface»
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
igorpecovnik commented Oct 2, 2015
ramki982 commented Oct 3, 2015
[FAILED] Failed to start Login Service.
See ‘systemctl status systemd-logind.service’ for details.
[ OK ] Started LSB: Get some info about hardware for some A. e basic things.
igorpecovnik commented Oct 3, 2015
ramki982 commented Oct 3, 2015
Thanks Igor, Do you have any clues as to why LOGIN service failed even if I used a static network configuration to get past that Ethernet issue?
igorpecovnik commented Oct 3, 2015
No clue at the moment, but am almost sure that systemd is the one which can’t cope with this situation. Try to build image this way: http://without-systemd.org/wiki/index.php/How_to_remove_systemd_from_a_Debian_jessie/sid_installation
ramki982 commented Oct 3, 2015
Let me try that & update you
ramki982 commented Oct 3, 2015
Is this difference in directory name giving u any clues?
Thx again for all your awesome work
ramki982 commented Oct 3, 2015
That older build based on 4.2-rc7 was built few weeks back
igorpecovnik commented Oct 3, 2015
ramki982 commented Oct 3, 2015
igorpecovnik commented Oct 3, 2015
This one works only on recent u-boot. Bottom up. Not a trivial task.
It’s not just kernel which can make you troubles 😉
ramki982 commented Oct 3, 2015
zador-blood-stained commented Oct 3, 2015
The thing is, day, month and time reads correctly in both cases, and only year is off by 70.
Comparing Mainline and Legacy RTC drivers, looks like they are using different offset for setting year on the RTC, which leads to 70 years difference.
Hope this helps.
zador-blood-stained commented Oct 3, 2015
ramki982 commented Oct 3, 2015
Can u share the diff to sunxi rtc driver so that I can try this. Thanks a bunch for sharing your findings
zador-blood-stained commented Oct 3, 2015
igorpecovnik commented Oct 3, 2015
zador-blood-stained commented Oct 3, 2015
zador-blood-stained commented Oct 4, 2015
By the way, Igor, you can have both systemd and sysvinit installed in Jessie, and switch between them by using different u-boot scripts, if you remove only systemd-sysv ( sysvinit-core should be installed instead of it).
To boot into systemd, you will need to add init=/bin/systemd to bootargs in boot.cmd, and without this parameter it will boot with sysvinit.
igorpecovnik commented Oct 4, 2015
zador-blood-stained commented Oct 4, 2015
From systemd bug discussion mentioned above I’m assuming that the reason for RTC issues is that mainline kernel might had switched from 32 bit time_t ( or another time related type) to 64 bit, so before instead of year 2085 we would just had an overflow and wrong date and time, but now we get all kinds of bugs in userspace.
Right now I’m compiling patched 3.4.109, and if it works like I want it to and doesn’t break anything, I will post patch here.
What do you mean by «u-boot has no effect»?
igorpecovnik commented Oct 5, 2015
It must be some general change/bug; it’s possible. I’ll wait if your patch brings the joy.
zador-blood-stained commented Oct 5, 2015
There are (or actually were) 2 or 3 separate bugs, unrelated to each other.
I believe that your last commit, that disables i2c debug messages, actually fixed last two. I think that systemd-journald and/or rsyslog were so busy processing i2c debug spam, that they locked up another services that tried to use logging subsystem.
I just unpacked recompiled kernel on clean Jessie 4.4 image (downloaded from armbian.com, still with systemd), and it works like a charm.
I consider RTC bug for now being a low priority, because it happens only when switching kernels, and it can be fixed manually relatively easy (if you want, I can post instructions here).
In my system evbug module (kernel config CONFIG_INPUT_EVBUG ) loads due to plugged keyboard and fills dmesg with debug messages related to keyboard events, please disable or blacklist it.
igorpecovnik commented Oct 5, 2015
zador-blood-stained commented Oct 5, 2015
If system is not booting after switching kernel from 3.4 to mainline due to systemd lockup, it can be fixed in-place without reflashing this way:
You have to get to u-boot command prompt, using either a serial adapter or monitor and usb keyboard.
After switching power on or rebooting, when u-boot loads up, press some keys on the keyboard (or send some key presses via terminal) to abort default boot sequence and get to the command prompt:
Enter these commands, replacing root device path if necessary.
Select setenv line with ttyS0 for serial, tty1 for keyboard+monitor:
System should eventually boot to bash shell:
Now you can check current date, correct it and upload it to RTC. Example:
hwclock will print error due to read-only file system, but it actually updates RTC.
Theoretically, using bash shell with access to rootfs, users with armbian broken after update can remount rootfs to r/w, enable systemd debug shell and on next reboot use it to bring up network manually and upgrade kernel from armbian repo (when it will be available), but it is a whole another story.
zador-blood-stained commented Oct 6, 2015
Did you test fresh built image or your old one with new kernel? I tested only 4.2.2 kernel with manual reconfiguration, and without this commit especially (which is temporary measure for migrating to 4.2.3). Can you extract kernel config file from your image (it is in /boot ) and check if it actually picked up i2c debug changes?
ramki982 commented Oct 6, 2015
I think it did not pick the i2c changes. I’m running a re-build after ensuring the latest config is present with the i2c fix. Hopefully this will fix it.
Thanks so much for your help
dllud commented Oct 8, 2015
I had this same issue on fresh install for Cubieboard 2, with the Armbian 4.4 jessie 4.2.2 image which is currently on the download page.
Building from the repo @414492474aa32db43364094d12d35933e7861afc solved it. Thus a new release is needed sooner than latter.
(BTW, @igorpecovnik congrats for your work on these build scripts. It took long but I had never built so much stuff (incl. a kernel) with so little effort. Keep it going!)
zador-blood-stained commented Oct 12, 2015
Tested a little bit on cubietruck with Jessie 4.5 mainline image. Worked for me.
igorpecovnik commented Oct 12, 2015
Nice idea, I’ll explore it.
igorpecovnik commented Oct 24, 2015
Workaround works & bug will eventually be fixed within kernel so closing this.
bwilcutt commented May 11, 2016
The worse part about systemd is you have no idea what it is doing and, therefore, no idea how to fix any issues. Even running systemctl «—test» gives errors «cannot run as root». What kind of app doesn’t run as root? Seriously, what? Ridiculous.
So, people crawl back to initd because it is more plain, well spoken, and understandable. Systemd fixes a problem that never existed, then complements the ‘fix’ by bringing more issues. Not good.
NetworkManager
NetworkManager is a program for providing detection and configuration for systems to automatically connect to networks. NetworkManager’s functionality can be useful for both wireless and wired networks. For wireless networks, NetworkManager prefers known wireless networks and has the ability to switch to the most reliable network. NetworkManager-aware applications can switch from online and offline mode. NetworkManager also prefers wired connections over wireless ones, has support for modem connections and certain types of VPN. NetworkManager was originally developed by Red Hat and now is hosted by the GNOME project.
Contents
Installation
Enable NetworkManager

Additional interfaces
Mobile broadband support
NetworkManager uses ModemManager for mobile broadband connection support.
It may be necessary to restart NetworkManager.service for it to detect ModemManager. After you restart it, re-plug the modem again and it should be recognized.
PPPoE / DSL support
Install rp-pppoe package for PPPoE / DSL connection support. To actually add PPPoE connection, use nm-connection-editor and add new DSL/PPPoE connection.
VPN support
NetworkManager since version 1.16 has native support for WireGuard, all it needs is the wireguard kernel module. Read the WireGuard in NetworkManager blog post for details.
Support for other VPN types is based on a plug-in system. They are provided in the following packages:
Usage
nmcli examples
List nearby Wi-Fi networks:
Connect to a Wi-Fi network:
Connect to a hidden Wi-Fi network:
Connect to a Wi-Fi on the wlan1 interface:
Disconnect an interface:
Get a list of connections with their names, UUIDs, types and backing devices:
Activate a connection (i.e. connect to a network with an existing profile):
Delete a connection:
See a list of network devices and their state:
Edit a connection
Firstly you need to get list of connections:
Here you can use the first column as connection-id used later. In this example we pick Wired connection 2 as a connection-id.
You have three methods to configure a connection Wired connection 2 after it has been created:
To remove a setting pass an empty field («») to it like this:
Front-ends
To configure and have easy access to NetworkManager, most users will want to install an applet. This GUI front-end usually resides in the system tray (or notification area) and allows network selection and configuration of NetworkManager. Various desktop environments have their own applet. Otherwise you can use #nm-applet.
GNOME
GNOME has a built-in tool, accessible from the Network settings.
KDE Plasma
Install the plasma-nm package. After that, add it to the KDE taskbar via the Panel options > Add widgets > Networks menu.
nm-applet
network-manager-applet is a GTK 3 front-end which works under Xorg environments with a systray.
To store connection secrets install and configure GNOME/Keyring.
Be aware that after enabling the tick-box option Make available to other users for a connection, NetworkManager stores the password in plain-text, though the respective file is accessible only to root (or other users via nm-applet ). See #Encrypted Wi-Fi passwords.
When you close the stalonetray window, it closes nm-applet too, so no extra memory is used once you are done with network settings.
In order to run nm-applet with such notifications disabled, start the applet with the following command:
Appindicator
As of version 1.18.0 Appindicator support is available in the official network-manager-applet package. To use nm-applet in an Appindicator environment start the applet with the following command:
networkmanager-dmenu
Configuration
NetworkManager will require some additional steps to be able run properly. Make sure you have configured /etc/hosts as described in Network configuration#Set the hostname section.
After editing a configuration file, the changes can be applied by running:
NetworkManager-wait-online
Be aware that this can cause other issues.
In some cases, the service will still fail to start successfully on boot due to the timeout setting being too short. Edit the service to change NM_ONLINE_TIMEOUT from 60 to a higher value.
Set up PolicyKit permissions
By default, all users in active local sessions are allowed to change most network settings without a password. See General troubleshooting#Session permissions to check your session type. In most cases, everything should work out of the box.
Some actions (such as changing the system hostname) require an administrator password. In this case, you need to add yourself to the wheel group and run a Polkit authentication agent which will prompt for your password.
For remote sessions (e.g. headless VNC), you have several options for obtaining the necessary privileges to use NetworkManager:
Proxy settings
NetworkManager does not directly handle proxy settings, but if you are using GNOME or KDE, you could use proxydriver AUR which handles proxy settings using NetworkManager’s information.
In order for proxydriver to be able to change the proxy settings, you would need to execute this command, as part of the GNOME startup process (see GNOME#Autostart).
Checking connectivity
To disable NetworkManager’s connectivity check, use the following configuration. This can be useful when connected to a VPN that blocks connectivity checks.
Captive portals

For those behind a captive portal, the desktop manager may automatically open a window asking for credentials. If your desktop does not, you can use capnet-assist package (however, it currently it has a broken NetworkManager dispatcher script). Alternatively, you can create a NetworkManager dispatcher script with the following content:
You will need to restart NetworkManager.service or reboot for this to start working. Once you do, the dispatcher script should open a login window once it detects you are behind a captive portal.
Another solution is captive-browser-git AUR based on Google Chrome.
DHCP client
By default NetworkManager uses its internal DHCP client. The internal DHCPv4 plugin is based on the nettools’ n-dhcp4 library, while the internal DHCPv6 plugin is made from code based on systemd-networkd.
To use a different DHCP client install one of the alternatives:
DNS management
NetworkManager’s DNS management is described in the GNOME project’s wiki page—Projects/NetworkManager/DNS.
DNS caching and conditional forwarding
NetworkManager has a plugin to enable DNS caching and conditional forwarding (previously called «split DNS» in NetworkManager’s documentation) using dnsmasq or systemd-resolved. The advantages of this setup is that DNS lookups will be cached, shortening resolve times, and DNS lookups of VPN hosts will be routed to the relevant VPN’s DNS servers. This is especially useful if you are connected to more than one VPN.
dnsmasq
Make sure dnsmasq has been installed. Then set main.dns=dnsmasq with a configuration file in /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/ :
Custom dnsmasq configuration
You can check the configuration file syntax with:
See dnsmasq(8) for all available options.

In addition, dnsmasq also does not prioritize upstream IPv6 DNS. Unfortunately NetworkManager does not do this (Ubuntu Bug). A workaround would be to disable IPv4 DNS in the NetworkManager config, assuming one exists.
DNSSEC
For dnsmasq to properly validate DNSSEC, thus breaking DNS resolution with name servers that do not support it, create the following configuration file:
systemd-resolved

NetworkManager can use systemd-resolved as a DNS resolver and cache. Make sure that systemd-resolved is properly configured and that systemd-resolved.service is started before using it.
You can enable it explicitly by setting main.dns=systemd-resolved with a configuration file in /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/ :
DNS resolver with an openresolv subscriber
If openresolv has a subscriber for your local DNS resolver, set up the subscriber and configure NetworkManager to use openresolv.
Because NetworkManager advertises a single «interface» to resolvconf, it is not possible to implement conditional forwarding between two NetworkManager connections. See NetworkManager issue 153.
This can be partially mitigated if you set private_interfaces=»*» in /etc/resolvconf.conf [5]. Any queries for domains that are not in search domain list will not get forwarded. They will be handled according to the local resolver’s configuration, for example, forwarded to another DNS server or resolved recursively from the DNS root.
Custom DNS servers
Setting custom global DNS servers
Setting custom DNS servers in a connection
Setting custom DNS servers in a connection (GUI)
Setting custom DNS servers in a connection (nmcli / connection file)
To setup DNS Servers per connection, you can use the dns field (and the associated dns-search and dns-options ) in the connection settings.
/etc/resolv.conf
NetworkManager also offers hooks via so called dispatcher scripts that can be used to alter the /etc/resolv.conf after network changes. See #Network services with NetworkManager dispatcher and NetworkManager(8) for more information.
Unmanaged /etc/resolv.conf
After that /etc/resolv.conf might be a broken symlink that you will need to remove. Then, just create a new /etc/resolv.conf file.
Use openresolv
To configure NetworkManager to use openresolv, set main.rc-manager=resolvconf with a configuration file in /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/ :
Firewall
You can assign a firewalld zone based on your current connection. For example a restrictive firewall when at work, and a less restrictive one when at home.
Network services with NetworkManager dispatcher
There are quite a few network services that you will not want running until NetworkManager brings up an interface. NetworkManager has the ability to start services when you connect to a network and stop them when you disconnect (e.g. when using NFS, SMB and NTPd).
Once the service is active, scripts can be added to the /etc/NetworkManager/dispatcher.d directory.
Scripts must be owned by root, otherwise the dispatcher will not execute them. For added security, set group ownership to root as well:
Make sure the file is executable.
The scripts will be run in alphabetical order at connection time, and in reverse alphabetical order at disconnect time. To ensure what order they come up in, it is common to use numerical characters prior to the name of the script (e.g. 10-portmap or 30-netfs (which ensures that the portmapper is up before NFS mounts are attempted).
Scripts will receive the following arguments:
Avoiding the dispatcher timeout
If the above is working, then this section is not relevant. However, there is a general problem related to running dispatcher scripts which take longer to be executed. Initially an internal timeout of three seconds only was used. If the called script did not complete in time, it was killed. Later the timeout was extended to about 20 seconds (see the Bugtracker for more information). If the timeout still creates the problem, a work around may be to use a drop-in file for the NetworkManager-dispatcher.service to remain active after exit:
Now start and enable the modified NetworkManager-dispatcher service.
Dispatcher examples
Mount remote directory with sshfs
Mounting of SMB shares
Some SMB shares are only available on certain networks or locations (e.g. at home). You can use the dispatcher to only mount SMB shares that are present at your current location.
The following script will check if we connected to a specific network and mount shares accordingly:
The following script will unmount all SMB shares before a software initiated disconnect from a specific network:
The following script will attempt to unmount all SMB shares following an unexpected disconnect from a specific network:
An alternative is to use the script as seen in NFS#Using a NetworkManager dispatcher:
Create a symlink inside /etc/NetworkManager/dispatcher.d/pre-down/ to catch the pre-down events:
Mounting of NFS shares
Use dispatcher to automatically toggle wireless depending on LAN cable being plugged in
The idea is to only turn Wi-Fi on when the LAN cable is unplugged (for example when detaching from a laptop dock), and for Wi-Fi to be automatically disabled, once a LAN cable is plugged in again.
Create the following dispatcher script[6], replacing LAN_interface with yours.
Note that there is a fail-safe for the case when the LAN interface was connected when the computer was last on, and then disconnected while the computer was off. That would mean the radio would still be off when the computer is turned back on, and with a disconnected LAN interface, you would have no network.
Use dispatcher to connect to a VPN after a network connection is established
In this example we want to connect automatically to a previously defined VPN connection after connecting to a specific Wi-Fi network. First thing to do is to create the dispatcher script that defines what to do after we are connected to the network.
Trying to connect with the above script may still fail with NetworkManager-dispatcher.service complaining about ‘no valid VPN secrets’, because of the way VPN secrets are stored. Fortunately, there are different options to give the above script access to your VPN password.
If that alone does not work, you may have to create a passwd-file in a safe location with the same permissions and ownership as the dispatcher script, containing the following:
The script must be changed accordingly, so that it gets the password from the file:
2: Alternatively, change the password-flags and put the password directly in the configuration file adding the section vpn-secrets :
Use dispatcher to disable IPv6 on VPN provider connections
Many commercial VPN providers support only IPv4. That means all IPv6 traffic bypasses the VPN and renders it virtually useless. To avoid this, dispatcher can be used to disable all IPv6 traffic for the time a VPN connection is up.
OpenNTPD
Dynamically set NTP servers received via DHCP with systemd-timesyncd
When roaming between different networks (e.g. a company’s LAN, WiFi at home, various other WiFi now and then) you might want to set the NTP server(s) used by timesyncd to those provided by DHCP. However, NetworkManager itself is not capable to communicate with systemd-timesyncd to set the NTP server(s).
The dispatcher can work around it.
Testing
To start the GNOME applet in non-xdg-compliant window managers like awesome:
For static IP addresses, you will have to configure NetworkManager to understand them. The process usually involves right-clicking the applet and selecting something like ‘Edit Connections’.
Tips and tricks
Encrypted Wi-Fi passwords
The passwords are accessible to the root user in the filesystem and to users with access to settings via the GUI (e.g. nm-applet ).
It is preferable to save the passwords in encrypted form in a keyring instead of clear text. The downside of using a keyring is that the connections have to be set up for each user.
Using GNOME Keyring
The keyring daemon has to be started and the keyring needs to be unlocked for the following to work.
Using KDE Wallet
If the option was selected previously and you un-tick it, you may have to use the reset option first to make the password disappear from the file. Alternatively, delete the connection first and set it up again.
Sharing internet connection over Wi-Fi
You can share your internet connection (e.g. 3G or wired) with a few clicks. Please note that a firewall may interfere with internet sharing.
You will need a Wi-Fi card which supports AP mode, see Software access point#Wi-Fi device must support AP mode for details.
Create the shared connection:
The connection will be saved and remain stored for the next time you need it.
Sharing internet connection over Ethernet
Scenario: your device has internet connection over Wi-Fi and you want to share the internet connection to other devices over Ethernet.
Now you should have a new option «Shared Internet» under the Wired connections in NetworkManager.
Checking if networking is up inside a cron job or script

Some cron jobs require networking to be up to succeed. You may wish to avoid running these jobs when the network is down. To accomplish this, add an if test for networking that queries NetworkManager’s nm-tool and checks the state of networking. The test shown here succeeds if any interface is up, and fails if they are all down. This is convenient for laptops that might be hardwired, might be on wireless, or might be off the network.
This useful for a cron.hourly script that runs fpupdate for the F-Prot virus scanner signature update, as an example. Another way it might be useful, with a little modification, is to differentiate between networks using various parts of the output from nm-tool; for example, since the active wireless network is denoted with an asterisk, you could grep for the network name and then grep for a literal asterisk.
Connect to network with secret on boot
By default, NetworkManager will not connect to networks requiring a secret automatically on boot. This is because it locks such connections to the user who makes it by default, only connecting after they have logged in. To change this, do the following:
Log out and log back in to complete.
OpenConnect with password in KWallet
While you may type both values at connection time, plasma-nm 0.9.3.2-1 and above are capable of retrieving OpenConnect username and password directly from KWallet.
Open «KDE Wallet Manager» and look up your OpenConnect VPN connection under «Network Management|Maps». Click «Show values» and enter your credentials in key «VpnSecrets» in this form (replace username and password accordingly):
Next time you connect, username and password should appear in the «VPN secrets» dialog box.
Ignore specific devices
Sometimes it may be desired that NetworkManager ignores specific devices and does not try to configure addresses and routes for them. You can quickly and easily ignore devices by MAC or interface-name by using the following in /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/unmanaged.conf :
After editing the file, run nmcli general reload as root. Afterwards you should be able to configure interfaces without NetworkManager altering what you have set.
Configuring MAC address randomization
MAC randomization can be used for increased privacy by not disclosing your real MAC address to the network.
NetworkManager supports two types MAC Address Randomization: randomization during scanning, and for network connections. Both modes can be configured by modifying /etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf or by creating a separate configuration file in /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/ which is recommended since the aforementioned configuration file may be overwritten by NetworkManager.
Randomization during Wi-Fi scanning is enabled by default, but it may be disabled by adding the following lines to /etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf or a dedicated configuration file under /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d :
MAC randomization for network connections can be set to different modes for both wireless and ethernet interfaces. See the GNOME blog post for more details on the different modes.
See the following GNOME blog post for more details.
Enable IPv6 Privacy Extensions
Configure a unique DUID per connection
The DHCPv6 Unique Identifier (DUID) is a value used by the DHCPv6 client to identify itself to DHCPv6 servers. NetworkManager supports 3 types of DUID:
If the internal NetworkManager’s DHCP client is in use (the default) it will identify itself with a global and permanent DUID-UUID generated from the machine-id ( /etc/machine-id ). This means that all connections share the same UUID, which may be a privacy breach.
Fortunately, NetworkManager is able to provide unique DUIDs per connection, derived from the connection’s stable-id and a per-host unique key. You can enable that by adding the following configuration under /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d :
Working with wired connections
By default, NetworkManager generates a connection profile for each wired ethernet connection it finds. At the point when generating the connection, it does not know whether there will be more Ethernet adapters available. Hence, it calls the first wired connection «Wired connection 1». You can avoid generating this connection, by configuring no-auto-default (see NetworkManager.conf(5) ), or by simply deleting it. Then NetworkManager will remember not to generate a connection for this interface again.
You can also edit the connection (and persist it to disk) or delete it. NetworkManager will not re-generate a new connection. Then you can change the name to whatever you want. You can use something like nm-connection-editor for this task.
Using iwd as the Wi-Fi backend
To enable the experimental iwd backend, first install iwd and then create the following configuration file:
Running in a network namespace
If you would like to run NetworkManager inside a network namespace (e.g., to manage a specific device which should be use by selected applications), bring the device down before moving it to the namespace:
otherwise NetworkManager will later fail to establish the connection with a device is strictly unmanaged error.
Automatically connect to VPN
NetworkManager can be set to automatically connect to a VPN when connecting to the internet, on a per network basis. The VPN connection itself can be added in GNOME’s NetworkManager front-end, but to make it automatically use the VPN nmcli must be used. Other front-ends might not have this limitation.
Then find the UUID of the VPN connection, and add that to connection.secondaries of the Internet connection:
Now when NetworkManager is restarted and you connect to the Internet connection you have configured, you should automatically get connected to the VPN.
Troubleshooting
No prompt for password of secured Wi-Fi networks
Network management disabled
When NetworkManager shuts down but the pid (state) file is not removed, you will see a Network management disabled message. If this happens, remove the file manually:
Problems with internal DHCP client
If you have problems with getting an IP address using the internal DHCP client, consider using another DHCP client, see #DHCP client for instructions. This workaround might solve problems in big wireless networks like eduroam.
DHCP problems with dhclient
If you have problems with getting an IP address via DHCP, try to add the following to your /etc/dhclient.conf :
Where aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff is the MAC address of this NIC. The MAC address can be found using the ip link show interface command from the iproute2 package.
3G modem not detected
Switching off WLAN on laptops
Sometimes NetworkManager will not work when you disable your Wi-Fi adapter with a switch on your laptop and try to enable it again afterwards. This is often a problem with rfkill. To check if the driver notifies rfkill about the wireless adapter’s status, use:
If one identifier stays blocked after you switch on the adapter you could try to manually unblock it with (where X is the number of the identifier provided by the above output):
Static IP address settings revert to DHCP
Due to an unresolved bug, when changing default connections to a static IP address, nm-applet may not properly store the configuration change, and will revert to automatic DHCP.
Next, you will want to make the default connection not connect automatically. To do so, run nm-connection-editor (not as root). In the connection editor, edit the default connection (e.g. «Auto eth0») and uncheck «Connect automatically». Click Apply and close the connection editor.
Cannot edit connections as normal user
Forget hidden wireless network
Since hidden networks are not displayed in the selection list of the Wireless view, they cannot be forgotten (removed) with the GUI. You can delete one with the following command:
This also works for any other connection.
VPN not working in GNOME
When setting up OpenConnect or vpnc connections in NetworkManager while using GNOME, you will sometimes never see the dialog box pop up and the following error appears in /var/log/errors.log :
This may need to be done for any other NetworkManager VPN plugins as well, but these are the two most common.
Unable to connect to visible European wireless networks
WLAN chips are shipped with a default regulatory domain. If your access point does not operate within these limitations, you will not be able to connect to the network. Fixing this is easy:
Automatic connect to VPN on boot is not working
The problem occurs when the system (i.e. NetworkManager running as the root user) tries to establish a VPN connection, but the password is not accessible because it is stored in the GNOME Keyring of a particular user.
A solution is to keep the password to your VPN in plaintext, as described in step (2.) of #Use dispatcher to connect to a VPN after a network connection is established.
You do not need to use the dispatcher described in step (1.) to auto-connect anymore, if you use the new «auto-connect VPN» option from the nm-applet GUI.
Systemd Bottleneck
Over time the log files ( /var/log/journal ) can become very large. This can have a big impact on boot performance when using NetworkManager, see: Systemd#Boot time increasing over time.
Regular network disconnects, latency and lost packets (WiFi)
NetworkManager does a scan every 2 minutes.
Some WiFi drivers have issues when scanning for base stations whilst connected/associated. Symptoms include VPN disconnects/reconnects and lost packets, web pages failing to load and then refresh fine.
If roaming is not important, the periodic scanning behavior can be disabled by locking the BSSID of the access point in the WiFi connection profile.
Unable to turn on Wi-Fi with Lenovo laptop (IdeaPad, Legion, etc.)

Unloading the ideapad_laptop module should fix this. (warning: this may disable the laptop keyboard and touchpad also!).
Turn off hostname sending
NetworkManager by default sends the hostname to the DHCP server. Hostname sending can only be disabled per connection not globally (Issue #584).
To disable sending your hostname to the DHCP server for a specific connection, add the following to your network connection file:
nm-applet disappears in i3wm
If you use the xfce4-notifyd.service for notifications you must edit the unit and add the following:
nm-applet tray icons display wrongly
Unit dbus-org.freedesktop.resolve1.service not found
If systemd-resolved.service is not started, NetworkManager will try to start it using D-Bus and fail:
This can be disabled with a configuration file in /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/ :
Secrets were required, but not provided
If you attempt to connect to a network using nmcli device wifi connect SSID password password and received the following error:
You can try deleting the connection profile and creating a new one:
You can also try disabling MAC address randomization:
WPA Enterprise connection with iwd
If you try to connect to an WPA Enterprise network like ‘eduroam’ with NetworkManager with the iwd backend then you will get the following error from NetworkManager:
This is because NetworkManager can not configure a WPA Enterprise network. Therefore you have to configure it using an iwd configuration file /var/lib/iwd/essid.8021x like described in iwd#WPA Enterprise.
Failed to request VPN secrets
If you get this error:
It is either because the password is empty or you have to set up PolicyKit permissions.